8.1. PACKET FORMATS
Packet formats for the RapidIO parallel physical layer are virtually identical to those used by the serial physical layer. Parallel RapidIO packets differ from Serial RapidIO packets in the following two ways. First, because Parallel RapidIO packets are transmitted on the same data lines as the control symbols and because the parallel interface does not use K-codes to delimit packets and symbols, the first bit of a parallel packet indicates that it is a packet and not a control symbol. This is represented as S = 0 in Figure 8.2. This bit is also repeated, inverted in bit position 5. The serial packet does not include an S-bit distinguishing it from a control symbol. Second, where the serial physical layer provides five bits of acknowledgement ID, the parallel physical layer provides only three bits of acknowledgement ID. This means that there is coverage for up to 32 outstanding transactions between two serial link ports. For the parallel interface there is coverage for only eight outstanding transactions between ports. The serial link interface coverage is higher because serial interfaces are more likely to operate over a longer distance and have more unacknowledged transactions active between ports.
Figure 8.2. Comparison of parallel and serial RapidIO headers
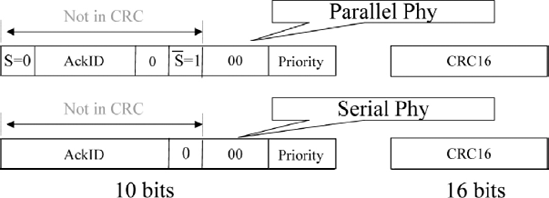
With the exception of these first six bits, there are no differences between the format of packets ...
Get RapidIO: The Next Generation Communication Fabric For Embedded Application now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

