Exercises
-
In a jump search algorithm, the optimum number of jumps required to attain the minimum cost of comparisons is
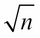 , where n is the length of the input vector. Can you derive it? Also, what is the cost of comparison for the worst case, when the number of jumps is
, where n is the length of the input vector. Can you derive it? Also, what is the cost of comparison for the worst case, when the number of jumps is 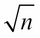 .
.
- Evaluate the cost of searching an unsorted and a sorted (sorting based on frequency) vector, where each element has an equal probability of being accessed during the search operation, under the following conditions:
- pi = 1/n, where i is the element in the given vector
- pi = 1/n2, where ...
Get R Data Structures and Algorithms now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

