SUMMARY OF LEARNING OBJECTIVES
- Describe how the cost principle applies to plant assets. The cost of a plant asset includes all expenditures necessary to acquire the asset and make it ready for its intended use. Cost is measured by the cash or cash equivalent price paid.
- Explain the concept of depreciation and how to compute it. Depreciation is the allocation of the cost of a plant asset to expense over its limited useful (service) life in a rational and systematic manner. Depreciation is not a process of valuation, nor is it a process that results in an accumulation of cash.
Three depreciation methods are:
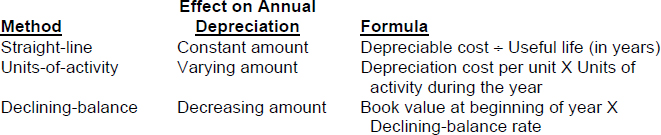
Companies make revisions of periodic depreciation in present and future periods, not retroactively. When the straight-line depreciation method is used, they determine the new annual depreciation by dividing the depreciable cost at the time of the revision by the remaining useful life.
- Distinguish between revenue and capital expenditures, and explain the entries for each. Companies incur revenue expenditures to maintain the operating efficiency and expected productive life of an asset. They debit these expenditures to Maintenance and Repairs Expense as incurred. Capital expenditures add new asset services or increase the operating efficiency, productive capacity, or expected useful life of the asset. Companies generally debit these expenditures to the plant asset affected.
- Explain ...
Get Problem Solving Survival Guide to accompany Financial Accounting, 8th Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

