2.5 SUMMARY OF A RANDOM EXPERIMENT
It will be useful at this point to summarize our description of a random experiment for which we want to assign a probability measure:
- The sample space Ω is the collection of all outcomes of an experiment. Depending on the type of experiment, it may contain a finite, countably infinite, or uncountable number of elements.
- An event of an experiment is a subset of Ω consisting of one or more outcomes, and which usually share some feature. Since the goal is to assign a probability measure to events that is consistent, we may not want to include all possible subsets of Ω.
- A σ-field
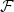 is a collection of subsets of Ω that satisfy the algebraic conditions in (i) and
is a collection of subsets of Ω that satisfy the algebraic conditions in (i) and 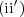 , as well as (iii), (iv), and
, as well as (iii), (iv), and 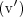 . One can envision constructing a σ-field by starting with some subset of Ω and expanding the number of subsets until the collection satisfies (i) and
. One can envision constructing a σ-field by starting with some subset of Ω and expanding the number of subsets until the collection satisfies (i) and 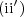 .
. - If Ω is finite or countably infinite, then all subsets described by the power set
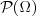 comprise a useful σ-field for the ...
comprise a useful σ-field for the ...
Get Probability, Random Variables, and Random Processes: Theory and Signal Processing Applications now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

