D.4 PDF INTEGRALS
The various pdfs covered in Chapter 3 and summarized in Appendix A are functions whose shapes are useful models for the random outcomes in various applications. Most of the pdfs include an exponential term as shown in Table D.1 where we have collected them into three groups (except the continuous uniform and triangular pdfs). The pdfs in the first group include an exponential function of x2 (or higher, as in the case of the Weibull distribution). The second group also includes an exponential function but of x, and the logistic and extreme value pdfs have two exponential functions. The third group of pdfs do not include any exponential functions, and depend on x with various exponents.
TABLE D.1 Pdf Functional Forms for Continuous Random Variables
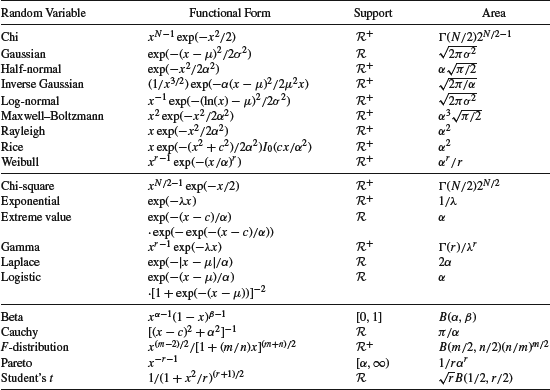
The area under each function and the support are also included in the table. The inverse of each term in the last column is the weighting applied to the functional form so that the pdf has unit area. It is the functional form that defines the pdf, and the weighting is just a constant for specific values of the pdf parameters. For example, consider the gamma random variable with pdf
(D.48) ![]()
where
(D.49) ![]()
is the gamma function ...
Get Probability, Random Variables, and Random Processes: Theory and Signal Processing Applications now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

