B.8 DIRAC DELTA FUNCTION
A generalized function is used to describe mappings that technically are not functions. Perhaps the most well-known generalized function is the Dirac delta function.
Definition: Dirac Delta Function The Dirac delta function is
(B.40) ![]()
However, this definition is not very useful; for example, it is not apparent how to multiply another function g(x) with δ (x). It turns out that we can define such a multiplication as follows:
(B.41) ![]()
where the right-hand side is still a delta function at the same location but now has area g(xo). This is the so-called sampling property of δ (x). The Dirac delta function is a convenient description of an impulse in physical systems. In particular, we are interested in how δ (x) behaves when filtered (via convolution) and when using integral transforms (such as the Fourier transform). From the sampling property:
(B.42) 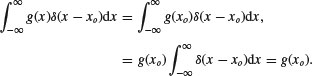
This result is the sifting property of δ (x) because it “sifts” out the value of the function g(x) (with which it is multiplied) at the location of the delta function.
We can also view (and define) the Dirac delta function as the limiting result of a unit-area rectangle as its width tends to zero and its height ...
Get Probability, Random Variables, and Random Processes: Theory and Signal Processing Applications now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

