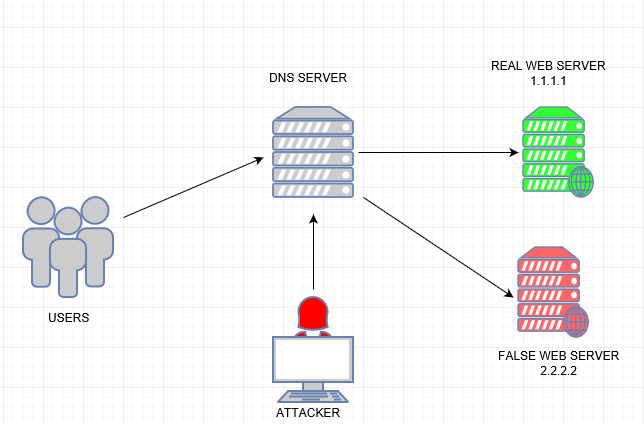
DNS spoofing or DNS cache poisoning: DNS spoofing occurs when particular DNS server records are altered to redirect traffic to the attacker. This redirection of traffic allows the attacker to steal data because it is hard for users to recognize the difference between an actual web page and a false web page.
In this example, users are trying to get the IP address for a real web server which is 1.1.1.1 but attackers have manipulated the DNS record and, consequently, users are redirected to the IP address for a fake website, which is 2.2.2.2: