The WAP Model
The WAP programming model is similar to the current HTTP model. WAP consists of a client, a gateway, and an origin server, as shown in Figure 22.1.
Figure 22.1. The WAP model.
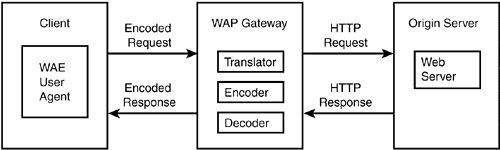
In looking at this figure, you can determine the following steps:
1. | The user makes a request for content. |
2. | The Wireless Application Environment (WAE) user agent encodes the request. |
3. | The WAE user agent sends the request to the gateway. |
4. | The gateway decodes the request. |
5. | The gateway translates the request (to HTTP) and sends it to the origin server. |
6. | The origin server passes back the appropriate content. |
7. | If necessary, the gateway translates the content ... |
Get PowerBuilder® 9: Internet and Distributed Application Development now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

