66 Broker Interactions for Intra- and Inter-enterprise
3.5 Data-focused application patterns
When applications need to share information rather than coordinate processing,
data-focused application integration is more appropriate than a process-focused
approach. Note, however, that when the frequency of data update is extremely
high (for example, when integrating an order entry system with a back-end ERP
system), process integration is the best solution. When this is not the case,
however, integration of (application) data repositories is handled outside of any
specific application request.
In delineating Data-focused Application Integration patterns, two key
environmental questions should be asked:
Is the enterprise data topology centralized or decentralized?
– Centralized: This integration effort will bring about centralized access to
all or a subset of the enterprise data model.
– Decentralized: Applications will retain their isolated repositories but now
with cohesion based on data integration.
What is the database affinity type?
– Homogeneous: All repositories are of the same type.
– Multi-vender Relational: All repositories are relational with ODBC/JDBC
support for interoperability but are from different vendors.
– Heterogeneous Structured: repositories are not all relational, but all
have a structured layout.
– Structured/Non-Structured: The need to integrate non-structured
(for example, free-form text) with structured data sources.
Refer to the IBM Patterns for e-business Web site for further details:
http://www.ibm.com/developerWorks/patterns
3.6 Previous Application Integration patterns
Table 3-3 provides an overview of the relationship between the previous
Process-focused Application Integration patterns and the revised
Process-focused Application Integration patterns presented in this chapter:
Direct Connection is retained for application coordinated requests.
Transactional is now a quality of service. Transactionality may apply to all of
these patterns, so it is applied as a quality of service rather than being a
separate pattern.
Aggregator/Broker are combined into Broker for broker coordinated requests.
Chapter 3. Application Integration pattern 67
Managed Process is split into Serial Process and Parallel Process for process
managed coordinated requests.
The read-only versus read/write classification used with old patterns is not
used with the new patterns, since:
– For Transactional and Managed Process, read-only is not applicable.
– For Direct Connection, the same pattern applies in both cases.
– For Aggregator/Broker, the observed patterns are identical.
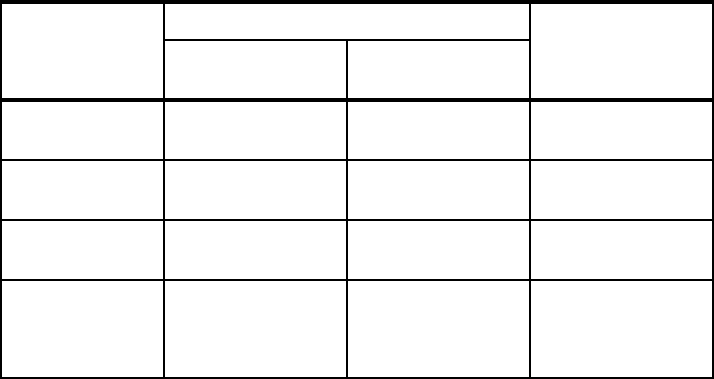
Table 3-3 Relationship to old Process-focused Application Integration patterns
Old Pattern New Pattern
Information
Request (R/O)
Processing
Request (R/W)
Application
Coordinated
Direct Connection Direct Connection Same
Transactional
Coordinated
Not applicable Transactional Now a Quality of
Service
Broker
Coordinated
Aggregator Broker Broker
Process
Managed
Coordinated
Not applicable Managed Process Split into:
Serial Process
Parallel Process
68 Broker Interactions for Intra- and Inter-enterprise
Get Patterns: Broker Interactions for Intra- and Inter-enterprise now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

