Chapter 9. System and Cloud Services
System services are those that are enabled by hardware features or provided by the Linux OS. Hardware-enabled services include access to accelerometer data, location services, and connection status. The OS provides alarms, sounds, power management, properties, and time services.
As described in Chapter 8, the Mojo framework provides access to the system services, routing requests to the specified services and calling the applicationâs callback functions with the service response. As shown in Figure 9-1, all system services are actually managed by Linux-resident server processes. The servers receive service requests from the application and send messages back. The messages are routed to the application through the specified callback functions, whether fulfilling the request or providing a failure indication.
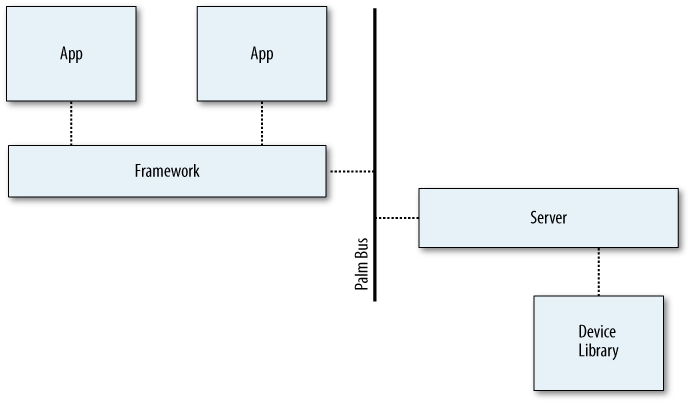
Figure 9-1. High-level service architecture
Cloud services are a form of web services. The initial cloud service is Mojo Messaging, an Extensible Messaging and Presence Prototocol (XMPP)-based messaging service for publish/subscribe notifications. It allows applications to send or receive notifications through the cloud to other collaborating clients and services. Over time there will be other cloud services that applications can leverage, extending the webOS platform further into the cloud.
Get Palm webOS now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

