Host Naming
Host naming is a TCP/IP-only solution that uses your existing IP address resolution method. To connect to a database, you simply specify the hostname of the database server. Net8 connects to that server and expects to find a database with a name matching the host—hence the term host naming. Figure 2.5 illustrates the process.
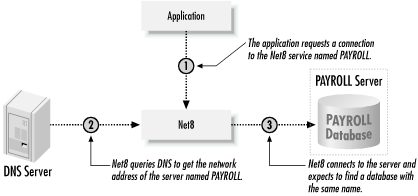
Figure 2-5. When host naming is used, Net8 expects to find a database with the same name as the server
The following rules apply to hostname resolution:
Host naming may only be used in TCP/IP environments.
Host naming requires the Domain Name Service (DNS) or some other TCP/IP name resolution mechanism—possibly a hosts file—to be in place to translate hostnames to network addresses.
The database name must match the name of the server hosting the database.
The last point (the database name and the server name have to match) is the most important. It is the fully qualified database name, which includes the domain, that must match the server name. Thus, if you are connecting to a server named jeff.gennick.org, your database parameter file must contain the following entries:
db_name = jeff db_domain = gennick.org
Since the database and server names must match, it appears at first glance that you can have only one database per server. That’s not entirely true. You can have multiple databases per server, but you have to define multiple names for the server in ...
Get Oracle Net8 Configuration and Troubleshooting now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

