Workflow Partitioning
Workflow partitioning refers to applications that are distributed across multiple databases, each of which is associated with a particular business function. The traditional example is the distributed system that has different sites allocated to order entry, shipping, and billing. These databases may or may not be at the same geographic location and may or may not be on the same network. As a general rule, the propagation mode for these applications is asynchronous. Figure 7.8 shows partitioning among three sites.
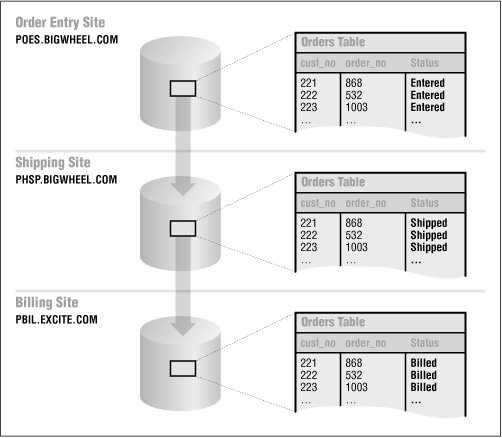
Figure 7-8. Workflow partitioning among three sites
An application that lends itself to workflow partitioning is an ideal candidate for multi-master table replication. Since the data updates that occur at each site are distinct, it is highly unlikely that conflicts will arise. And the probability of conflicts can be reduced significantly by incorporating business rules into the application. For example, in the previous example, an order cannot be billed until it has shipped. Also, Oracle provides built-in conflict resolution methods that are specifically designed for workflow partitioning, such as priority groups. Refer to Chapter 15 for details about implementing priority groups and other conflict resolution techniques.
As with other advanced replication architectures, workflow partitioning must cope with the latency inherent in asynchronous propagation. ...
Get Oracle Distributed Systems now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

