CHAPTER 8Application of Islamic Products to Private Equity
Private equity is not always a separate division within a bank, but can also occur as part of the corporate finance division or treasury. Due to the fact that a private equity investment represents a direct investment in an enterprise and the investor is taking a business risk, investments in public as well as private equity are looked upon favourably by Sharia'a scholars. The two different structures as described in Chapter 3 that are suitable for private equity investments are musharaka and mudaraba transactions.
In a joint venture of musharaka structure, all partners provide capital and skills and expertise to the project. Profits are shared based on a contractually agreed ratio between the partners and any losses are distributed in accordance with the proportion of capital provided. The bank often opts to become a sleeping partner and leaves the running of the business to the other partners, potentially in return for a lower share in the profits.
Musharaka transactions (Figure 8.1) are typically suitable for investments in business ventures or specific business projects, and need to consist of at least two parties, and all partners are known as musharik.
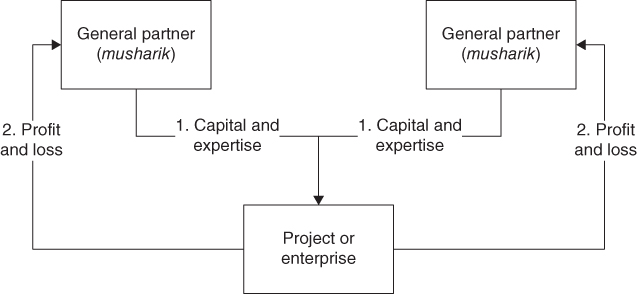
Figure 8.1 Musharaka transaction for private equity
Another option for private equity investment, besides the musharaka transaction, is the mudaraba, a partnership ...
Get Modern Islamic Banking now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

