6.4 Specificities for Parameter Identification, Calibration or Data Assimilation Algorithms
As shown in the previous sections, parameter identification or calibration algorithms identify the ‘central value’ of the input variables, X being replaced by a fixed (although unknown) parameter xm, representing, for instance, system properties in a mechanical model or initial conditions in a meteorological model. A review of the particular features will be given for those cases, expanding to the general domain of data assimilation and parameter identification, and the main existing algorithms.
6.4.1 The BLUE Algorithm for Linear gaussian Parameter Identification
Consider the simplest formulation where the system model is linear (or linearised), the uncertainty model is Gaussian and where data only is assimilated to estimate the value xm in absence of any prior expertise available. The program to be estimated is the following:
(6.130) 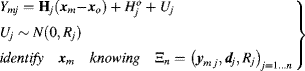
The BLUE Estimator
The log-likelihood is the following quadratic function of xm:
(6.131) ![]()
the maximisation of which enjoys the following closed-form solution (refer for a demonstration onto the general solution of a quadratic program given in Annex Section 10.5.2):
(6.132)
It may be seen as an algebraic n-dimensional generalisation of the estimator that was ...
Get Modelling Under Risk and Uncertainty: An Introduction to Statistical, Phenomenological and Computational Methods now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

