This score is complementary to the previous one. Its purpose is to provide a piece of information about the assignment of samples belonging to the same class. More precisely, a good clustering algorithm should assign all samples with the same true label to the same cluster. From our previous analysis, we know that, for example, the digit 7 has been wrongly assigned to both clusters 9 and 1; therefore, we expect a non-perfect completeness score. The definition is symmetric to the homogeneity score:
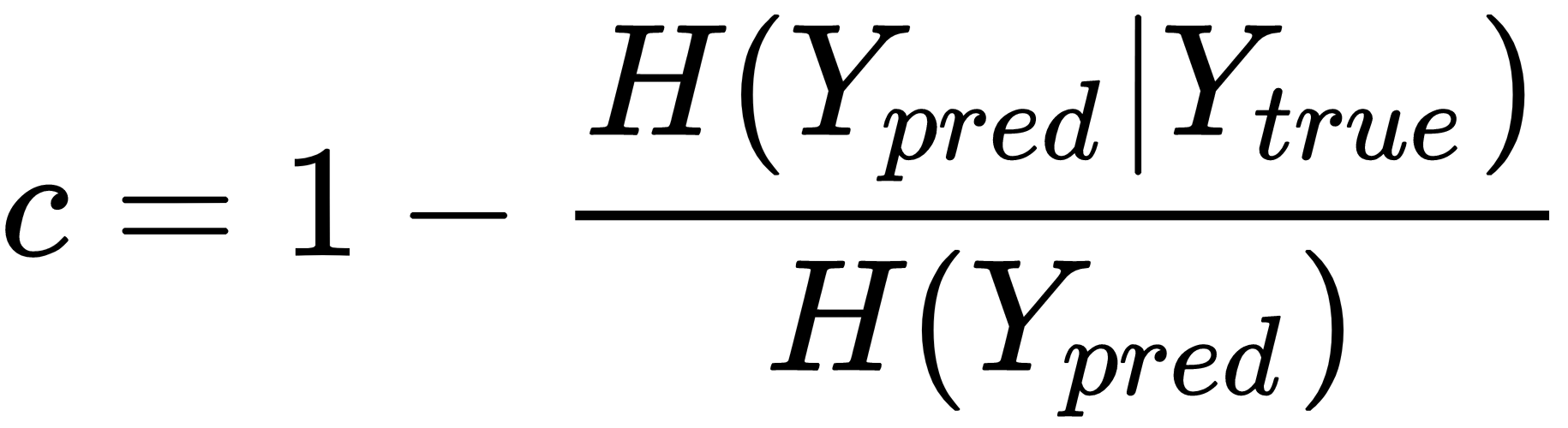
The rationale is very intuitive. When H(Ypred|Ytrue) is low (c → 1), it means that the knowledge of the ground truth reduces ...

