The most common type of convolution employed in deep learning is based on bidimensional arrays with any number of channels (such as grayscale or RGB images). For simplicity, let's analyze a single layer (channel) convolution because the extension to n layers is straightforward. If X ∈ ℜw × h and k ∈ ℜn × m, the convolution X ∗ k is defined as (the indexes start from 0):
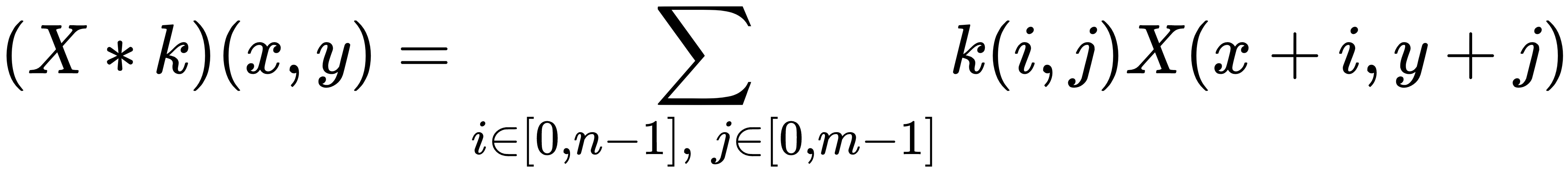
It's clear that the previous expression is a natural derivation of the continuous definition. In the following graph, there's an example with a 3 × 3 kernel:
The kernel is shifted horizontally ...

