The covariance matrix Σ is real and symmetric. If we apply the eigendecomposition, we get (for our purposes it's more useful to keep V-1 instead of the simplified version VT):
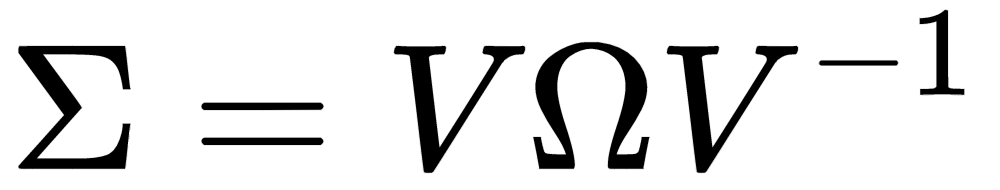
V is an orthogonal matrix (thanks to the fact that Σ is symmetric) containing the eigenvectors of Σ (as columns), while Ω is a diagonal matrix containing the eigenvalues. Let's suppose we sort both eigenvalues (λ1, λ2, ..., λm) and the corresponding eigenvectors (v1, v2, ..., vm) so that:
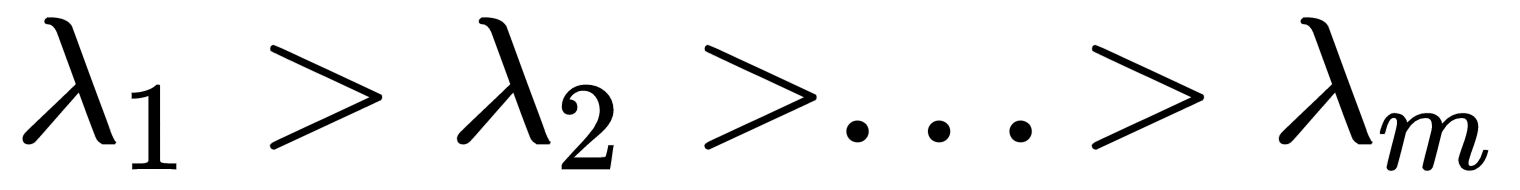
Moreover, let's suppose that λ1 is dominant over ...

