This algorithm, based on the spectral decomposition of a graph Laplacian, has been proposed in order to perform a non-linear dimensionality reduction to try to preserve the nearness of points in the P-dimensional manifold when remapping on a Q-dimensional (with Q < P) subspace.
The procedure is very similar to the other algorithms. The first step is a k-nearest neighbor clustering to generate a graph where the vertices (we can assume to have N elements) are the samples, and the edges are weighted using an RBF kernel:
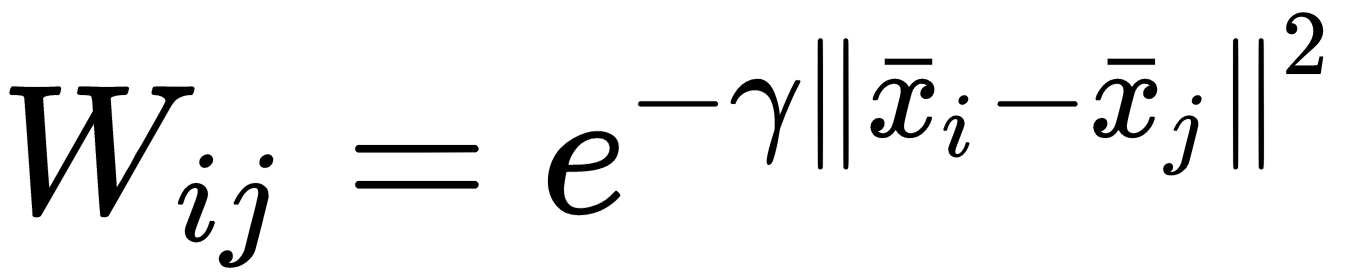
The resulting graph is undirected and symmetric. We can now define a pseudo-degree matrix D:

