Implementation and Analysis of Counting Sort
Counting sort works fundamentally by counting how many
times integer elements occur in an unsorted set to determine how the
set should be ordered. In the implementation presented here,
data initially contains the unsorted set of
size integer elements stored in a single
block of contiguous storage. Additional storage is allocated to store
the sorted data temporarily. Before ctsort
returns, the sorted set is copied back into
data.
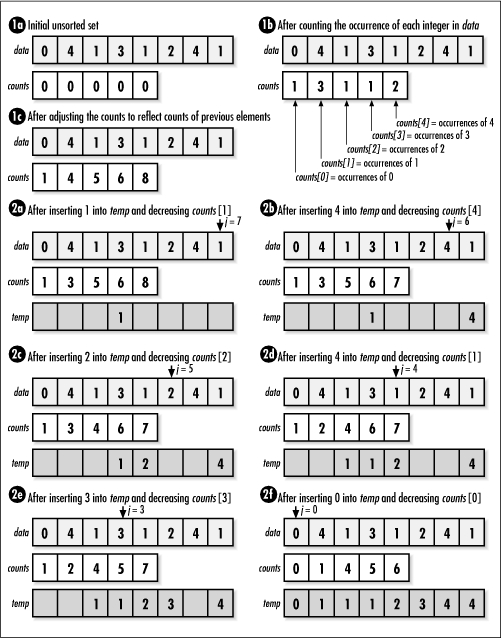
After allocating storage, we begin by counting the occurrences
of each element in data (see Example 12.6). These are placed in an
array of counts, counts, indexed by the
integer elements themselves (see Figure
12.6, step 1b). Once the occurrences of each element in
data have been counted, we adjust the
counts to reflect the number of elements that will come before each
element in the sorted set. We do this by adding the count of each
element in the array to the count of the element that follows it (see
Figure 12.6, step 1c). Effectively,
counts then contains the offsets at which
each element belongs in the sorted set,
temp.
To complete the sort, we place each element in
temp at its designated offset (see Figure 12.6, steps 2a- f ). The count for
each element is decreased by 1 as temp is
updated so that integers appearing more than once in
data appear more than once in
temp as well.
Get Mastering Algorithms with C now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

