14.8 Flat Architecture
3GPP Release 6 network architecture has four network elements in the user and control plane: base station (NodeB), RNC (Radio Network Controller), SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) and GGSN (Gateway GPRS Support Node). The architecture in Release 8 LTE has only two network elements: base station in the radio network and Access Gateway (a-GW) in the core network. The a-GW consists of control plane MME (Mobility management entity) and user plane SAE GW (System Architecture Evolution Gateway). The flat network architecture reduces the network latency and thus improves the overall end user performance. The flat model also improves both user and control plane efficiency. The flat architecture is considered beneficial also for HSPA and it is specified in Release 7. The HSPA flat architecture in Release 7 and LTE flat architecture in Release 8 are exactly the same: NodeB responsible for the mobility management, ciphering, all retransmissions and header compression both in HSPA and in LTE. The architecture evolution in HSPA is designed to be backwards compatible: existing terminals can operate with the new architecture and the radio and core network functional split is not changed. The architecture evolution is illustrated in Figure 14.13.
Figure 14.13 Evolution towards flat architecture.
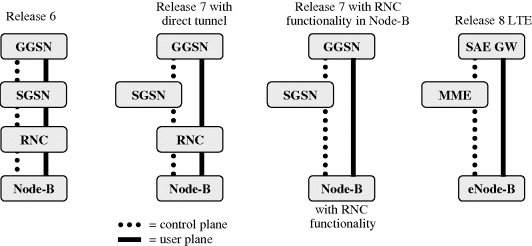
Also the packet core network has flat architecture in Release 7. It is called ...
Get LTE Advanced: 3GPP Solution for IMT-Advanced now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

