13.3 Radio Network Architecture Options
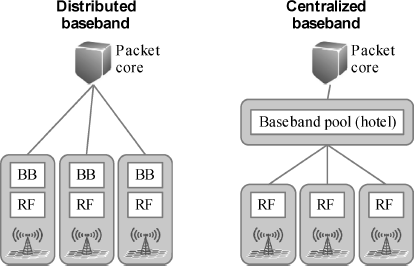
Release 8 LTE radio networks are designed to be distributed where all the radio network functionalities are located in the base station. Frequency domain inter-cell coordination in Release 8 can be obtained with a distributed architecture with slow information exchange between base stations, or even completely distributed algorithms based on the feedback from the terminals. More advanced real-time inter-cell interference coordination such as CoMP would benefit from a common and centralized control unit that could optimize the transmissions from multiple cells on a small time scale. Therefore, CoMP features can also have a major impact on the radio network architecture and the transport requirements. Figure 13.3 illustrates the two extreme architecture options: Distributed baseband and centralized baseband. The distributed baseband is the normal solution in LTE networks. The centralized baseband uses simple RF heads at the base station site connected over high speed fibre to the baseband pool, also called a baseband hotel.
Figure 13.3 Distributed and centralized baseband (BB = Baseband, RF = Radio Frequency).
Let's look quickly back at the history of radio network architecture. The original idea in WCDMA radio was to have the radio intelligence in the Radio Network Controller (RNC) while the base station only included RF and Layer 1 encoding ...
Get LTE Advanced: 3GPP Solution for IMT-Advanced now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

