3.2 Physical Layer
The LTE multiple access is based on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) in the downlink direction and on the Single Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) in the uplink direction.
The OFDMA parameterization is based on the 15 kHz sub-carrier spacing to ensure sufficient robustness to large velocity and frequency error, while at the same time the resulting sampling rates allow to have compatibility with the WCDMA sampling rates to facilitate easier multimode implementation both in the UE and the network side. The ODFMA transmitter and receiver chain example is shown in Figure 3.1.
Figure 3.1 LTE downlink OFDMA principle.
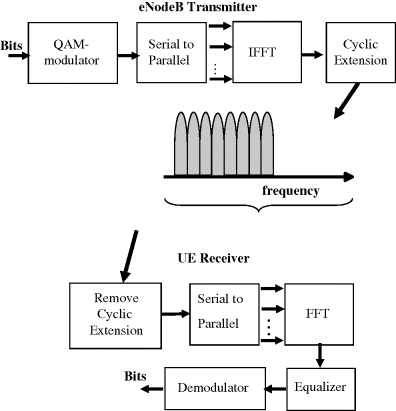
In the uplink direction the SC-FDMA facilitates power efficient terminal transmitter implementation since there are no parallel waveforms transmitted but the transmission principle is based on the use of a digital QAM modulation coupled with the cyclic prefix use after a block of symbols. The Peak to Average Ratio (PAR) or more specifically Cubic Metric (CM) is lower with SC-FDMA than with OFDMA, thus allowing avoiding the use of efficient power amplifier without excessive power back-off to maximize the uplink range, as presented in more details in [1].
Adding a cyclic prefix after every QAM symbol is not feasible due to the short symbol duration in time, which would result in massive overheads. Now the addition ...
Get LTE Advanced: 3GPP Solution for IMT-Advanced now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

