14.3 Binomial
The binomial distribution has two parameters, m and q. Frequently, the value of m is known and fixed. In this case, only one parameter, q, needs to be estimated. In many insurance situations, q is interpreted as the probability of some event such as death or disability. In such cases, the value of q is usually estimated as
![]()
which is the method-of-moments estimator when m is known.
In situations where frequency data are in the form of the previous examples in this chapter, the value of the parameter m, the largest possible observation, may be known and fixed or unknown. In any case, m must be no smaller than the largest observation. The loglikelihood is
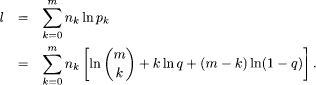
When m is known and fixed, one need only maximize l with respect to q:
![]()
Setting this expression equal to zero yields
![]()
which is the sample proportion of observed events. For the method of moments, with m fixed, the estimator of q is the same as the mle because the moment equation is
![]()
When m is unknown, the maximum likelihood ...
Get Loss Models: From Data to Decisions, 4th Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

