Configuring RSVP-Signaled LSPs
Imagine that you have a network where you're carrying a lot of voice traffic. You want to make sure that voice traffic gets forwarded along a path that has enough bandwidth to support the load without congestion. And because voice packets can't be received out of order, you want the entire voice flow to travel over the same path, as shown in Figure 16-4.
In this topology, you have a source of voice traffic (router 1) that is aggregating all your voice flows from various branch sites. You want to transport this data to headquarters, which requires sending the traffic through router 5 and off through the network and eventually to your headquarters.
You want to ensure that you have reserved bandwidth for all your flows, so you're going to use RSVP as your LSP signaling protocol. To configure the LSP across your network, you must
- Enable MPLS and RSVP on your router.
- Enable RSVP and RSVP on your transit interfaces.
- Configure your IGP to support traffic engineering.
- Set up an LSP from the ingress to the egress router.
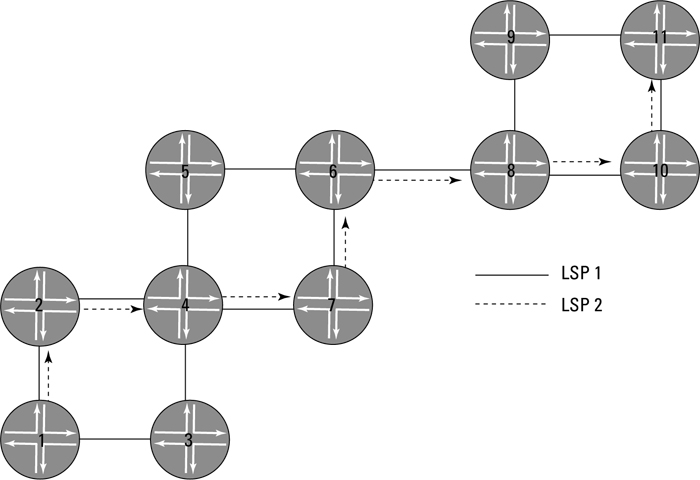
Figure 16-4: An MPLS network using RSVP.
Enabling MPLS and RSVP
Assuming that you've already set up your IGP and other routing protocols, the first thing you need to do to establish an RSVP LSP across your network is to enable both MPLS and RSVP on your routers.
You have to enable MPLS and RSVP across all the routers in your network, not ...
Get Junos® OS For Dummies®, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

