5.1 General Tax Rules for Property Sales
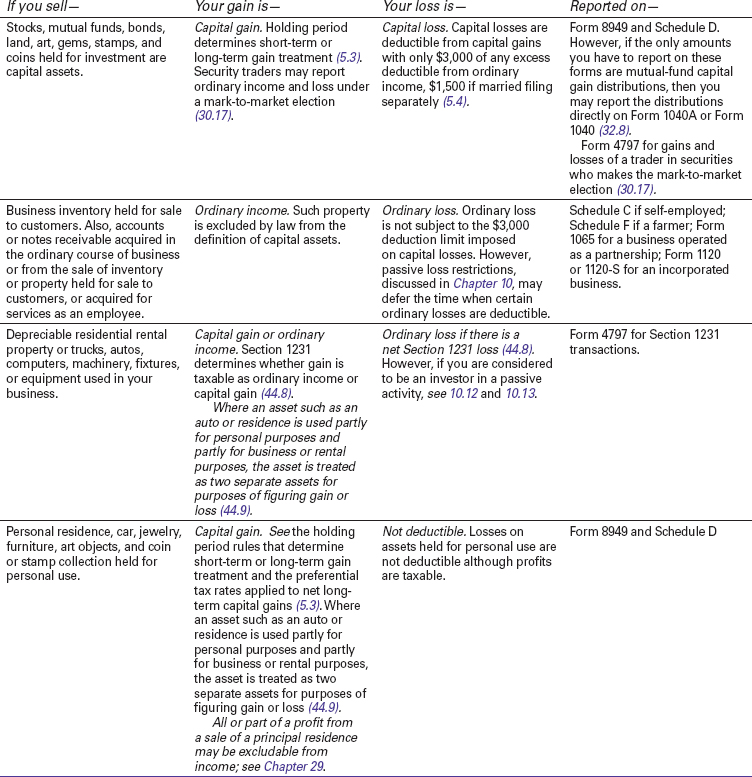
Table 5-1 Capital or Ordinary Gains and Losses From Sales and Exchanges of Property
Get J.K. Lasser's Your Income Tax 2013: For Preparing Your 2012 Tax Return now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

