Ambiguity Errors
The inclusion of generics gives rise to a new type of error that you must guard against: ambiguity. Ambiguity errors occur when erasure causes two seemingly distinct generic declarations to resolve to the same erased type, causing a conflict. Here is an example that involves method overloading:
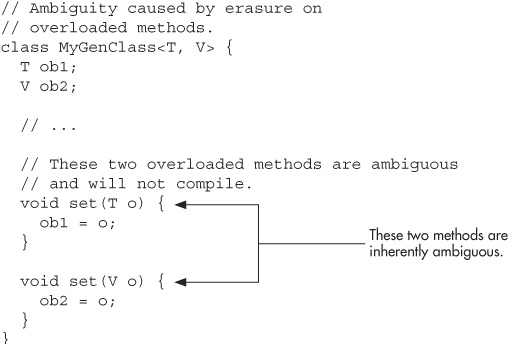
Notice that MyGenClass declares two generic types: T and V. Inside MyGenClass, an attempt is made to overload set( ) based on parameters of type T and V. This looks reasonable because T and V appear to be different types. However, there are two ambiguity problems here.
First, as MyGenClass is written there is no requirement that T and ...
Get Java, A Beginner's Guide, 5th Edition, 5th Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

