8.4. Profiles
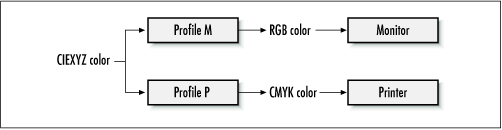
One way to compensate for device dependencies is by using a profile. A profile is a set of information that describes how to map from a standard color space (like CIEXYZ or sRGB) to the color space of a particular device. A color specified in CIEXYZ could be mapped, through the use of profiles, to the RGB spaces of each monitor. Assuming the profiles were correct, the color would appear the same on both monitors. The International Color Consortium (ICC) has a standard format for profiles (see http://www.color.org/). Figure 8.3 shows how a CIEXYZ color can be shown on two different output devices. The first profile is used to translate from a CIEXYZ color to an RGB color that the monitor can display. The second profile translates from CIEXYZ to the printer's CMYK color space.
Figure 8.3. Using profiles with output devices
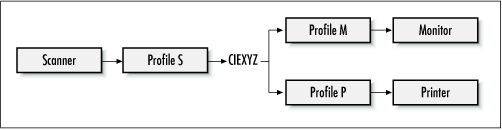
Color profiles are also useful for input devices. Figure 8.4 shows how a color can be accurately scanned and reproduced using color profiles. Initially, the color is defined in the scanner's color space. Profile S is used to convert this color to CIEXYZ. From there, it can be displayed on any output device, using an appropriate profile.
Figure 8.4. Profiles are useful with input devices, too
So where do profiles come from? The manufacturer of an ...
Get Java 2D Graphics now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

