NBMA Networks
Remember how a DR is elected -- basic to DR election is the broadcast or multicast capability of the underlying network. NBMA networks such as Frame Relay or X.25 have no inherent broadcast or multicast capability, but they can simulate a broadcast network if fully meshed. However, a fully meshed network with n nodes requires n x (n-1)/2 virtual circuits. The cost of n x (n-1)/2 virtual circuits may be unpalatable, and besides, the failure of a single virtual circuit would disrupt this full mesh.
One option around a fully meshed network is to (statically) configure the DR for the network. The DR will then advertise the NBMA network as a multi-access network using a single IP subnet in a network LSA.
Another option is to configure the network as a set of point-to-point networks. This is simpler to configure, manage, and understand. However, each point-to-point network wastes an IP subnet. So what? You can use VLSM in OSPF, with a two-bit subnet for each point-to-point network. That is a good argument. However, the trade-off is the processing overhead of an LSA for each point-to-point network.
Let’s look at examples of each of these options.
NewYork2 is set up with a serial interface to support Frame Relay PVCs to offices in Miami and New Orleans, as shown in Figure 6-12.
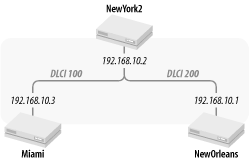
Figure 6-12. TraderMary’s Frame Relay network
The command ip ospf network broadcast (lines 52, 53, and ...
Get IP Routing now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

