Chapter 8
MPLS Technology – Fault Management
8.1. Introduction
Fault management refers to the reconfiguration of the Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) network in instances of node or link loss, and the reconfiguration of the label switching router (LSR) equipment when failure of the processor card supporting the control plane occurs.
The MPLS network has two operating modes, depending on whether or not traffic engineering is being used. The difference between these two modes lies in the types of control protocols implemented:
– the open shortest path first (OSPF) routing protocol and the label distribution protocol (LDP) in the absence of traffic engineering (TE);
– the OSPF-TE routing protocol and the ReSerVation Protocol traffic engineering (RSVP-TE) label distribution and resource reservation protocol for TE.
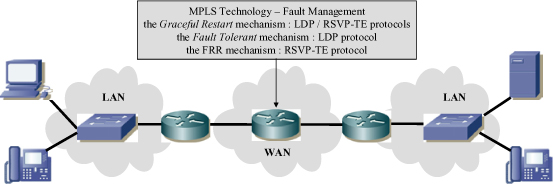
In the absence of TE, the routing and label distribution protocols carry out network reconfiguration when the fault occurs within the wide area network (WAN). This is obtained by updating the Routing (RIB), Forwarding (FIB), Label (LIB), and Label Forwarding (LFIB) Information Base tables following a change in topology (Figure 8.1).
When TE is present, the FRR (Fast ReRoute) mechanism based on the RSVP-TE protocol provides global or local protection, bypassing the faulty element (a link or node; Figure 8.1).
Figure 8.1. MPLS technology – fault management
Reconfiguring ...
Get IP, Ethernet and MPLS Networks: Resource and Fault Management now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

