Notes on Precedence and Type-of-Service
Applications can use the Precedence and Type-of-Service flags to dictate specific per-datagram handling instructions to the hosts and routers that forward the datagrams through a network. For example, the Precedence flags allow applications to set specific prioritization flags on the datagrams they generate, allowing them to define a higher-priority over normal traffic. Using this field, a database client could flag all IP datagrams with a higher priority than normal, which would inform the routers on the network to prioritize the database traffic over normal or lower-priority traffic.
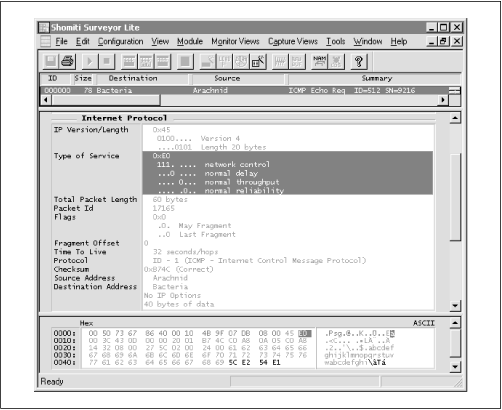
Figure 2.28 shows an ICMP Echo Request Query Message sent from Arachnid to Bacteria, with a Precedence value of 7 in the IP header’s Type-of-Service field. This IP packet would be given a higher priority over any other packets with a lower priority value, assuming the router supported this type of special handling operation (many routers do not offer this type of support).
Besides prioritization, the Type-of-Service byte also offers a variety of different special-handling flags that can also be used to dictate how a particular datagram should be treated. A Telnet client could set the “Minimize Latency” Type-of-Service flag on the datagrams that it generated, requesting that routers forward that traffic across a faster ...
Get Internet Core Protocols: The Definitive Guide now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

