14.6 ‘Within’ Variability and ‘Overall’ Variability
14.6.1 What Are They?
Within refers to the within samples variation. It gives an idea of the variability observed within a short period of time (also called ‘short-term’ variability) without taking into account causes like raw material changes, machine fouling, operator shifts, etc. that will inevitably appear. It can be interpreted as the minimal variability that can be achieved if all causes affecting the process along time were eliminated.
Overall refers to the global variability of the data, also called ‘long-term’ variability. It is the real variability of the production process.
14.6.2 How Are They Computed?
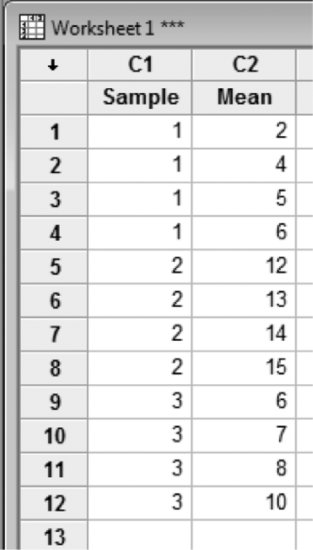
Let's use the simple set of numbers displayed on the right to illustrate the difference between both types of variability and to show how to compute them.
We have only three subgroups, each containing each four observations.
Variability within the Subgroups (‘Within’):
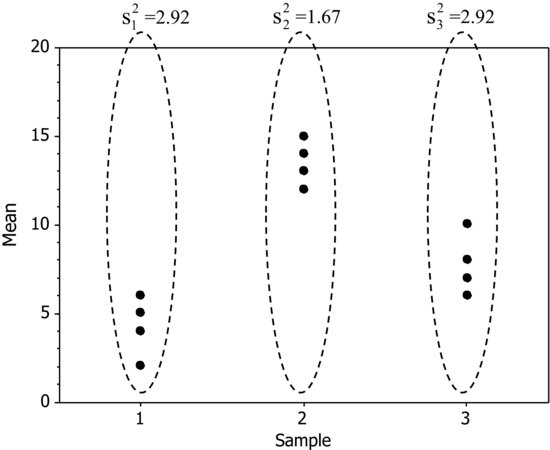
The best estimator of the variance within subgroups is the mean of the subgroup variances. In our case:
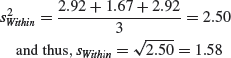
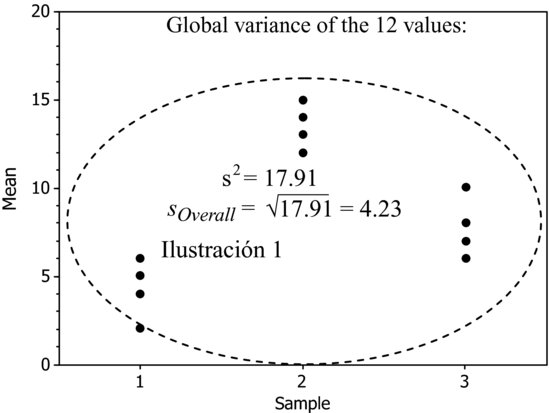
Global Variability (Overall)
To carry out a ...
Get Industrial Statistics with Minitab now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

