7.4 Noise Power from Parallel Systems
Often there will be more than one noise signal (noise power sources) present at the input of a system. This could be two parts of an active DAS, using two repeaters, that needs to be combined to a base station receiver, like the GSM (200 kHz) example in Figure 7.13.
Figure 7.13 Two parallel noise sources combined into one output
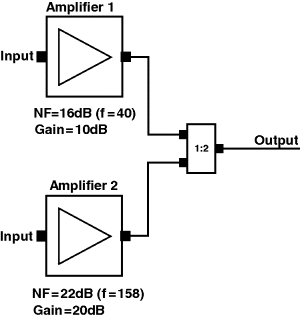
7.4.1 Calculating Noise Power from Parallel Sources
Random Power Signals
Noise is random (white noise), and two noise signals will be noncorrelated. Thus the noise powers (in Watts) of two sources can be added in order to calculate the total noise power from the system.
First we need calculate the noise floor for each of the two amplifiers (GSM):
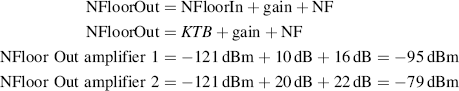
Watts
We need to sum up the noise, by adding the power contribution from each source.
![]()
Now we convert the noise powers from dBm to mW:
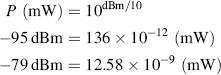
Then we can sum up the two powers:
![]()
Convert to dBm
We convert the noise power back to dBm:
The Combiner
The noise power is combined in a splitter ...
Get Indoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for GSM, DCS, UMTS, HSPA and LTE, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

