Chapter 2. IBM System Networking Switch 10Gb Ethernet switch features 105
2.9.6 QoS 802.1p
IBM Networking OS provides Quality of Service functions based on the priority bits in a
packet’s VLAN header. (The priority bits are defined by the 802.1p standard within the IEEE
802.1q VLAN header.) The 802.1p bits, if present in the packet, specify the priority that
should be given to packets during forwarding. Packets with a numerically higher (non-zero)
priority are given forwarding preference over packets with lower priority bit value.
The IEEE 802.1p standard uses eight levels of priority (0 - 7). Priority 7 is assigned to highest
priority network traffic, such as OSPF or RIP routing table updates, priorities 5 - 6 are
assigned to delay-sensitive applications, such as voice and video, and lower priorities are
assigned to standard applications. A value of 0 (zero) indicates a “best effort” traffic
prioritization, and this value is the default when traffic priority is not configured on your
network. The VFSM can filter packets based on the 802.1p values, and it can assign or
overwrite the 802.1p value in the packet.
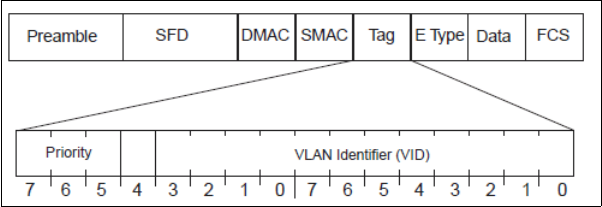
Figure 2-24 Layer 2 802.1q/802.1p tagged frame
Ingress packets receive a priority value, as follows:
Tagged packets: The switch reads the 802.1p priority in the VLAN tag.
Untagged packets: The switch tags the packet and assigns an 802.1p priority value,
based on the port’s default 802.1p priority.
Egress packets are placed in a COS queue based on the priority value, and scheduled for
transmission based on the COS queue number. Higher COS queue numbers provide
forwarding precedence.
2.9.7 Queuing and scheduling
IBM System Networking switches can be configured to have either two or eight output Class
of Service (COS) queues per port, into which each packet is placed. Each packet’s 802.1p
priority determines its COS queue, except when an ACL action sets the COS queue of
the packet.
You can configure the following attributes for COS queues:
Map 802.1p priority value to a COS queue.
Define the scheduling weight of each COS queue.
The scheduling weight can be set 0 - 15. Weight values 1 - 15 set the queue to use weighted
round-robin (WRR) scheduling, which distributes larger numbers of packets to queues with
the highest weight values. For distribution purposes, each packet is counted the same,
regardless of the packet’s size.

106 Implementing IBM System Networking 10Gb Ethernet Switches
A scheduling weight of 0 (zero) indicates strict priority. Traffic in the strict priority queue has
precedence over other all queues. If more than one queue is assigned a weight of 0, the strict
queue with highest queue number is served first. After all traffic in strict queues is delivered,
any remaining bandwidth is allocated to the WRR queues, divided according to their
weight values.
Strict scheduling: Use caution when assigning strict scheduling to queues. Heavy traffic
in queues assigned with a weight of 0 can starve lower priority queues.
Get Implementing IBM System Networking 10Gb Ethernet Switches now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

