Chapter 2. IBM System Networking Switch 10Gb Ethernet switch features 101
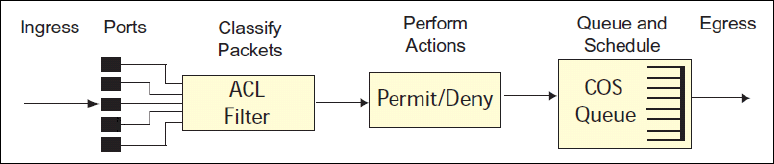
Figure 2-22 shows the basic QoS model used by the switch:
Figure 2-22 QoS model
The basic QoS model works as follows:
Classify traffic:
– Read DSCP value.
– Read 802.1p priority value.
– Match ACL filter parameters.
Perform actions:
– Define bandwidth and burst parameters.
– Select actions to perform on in-profile and out-of-profile traffic.
– Deny packets.
– Permit packets.
– Mark DSCP or 802.1p priority.
– Set COS queue (with or without re-marking).
Queue and schedule traffic:
– Place packets in one of the COS queues.
– Schedule transmission based on the COS queue.
2.9.2 Using ACL filters
ACLs are filters that you can use to classify and segment traffic, so you can provide different
levels of service to different traffic types. Each filter defines the conditions that must match for
inclusion in the filter, and also the actions that are performed when a match is made.
You can use IBM System Networking switches to classify packets based on various
parameters. For example:
Ethernet: Source MAC, destination MAC, VLAN number/mask, Ethernet type, and priority.
IPv4: Source IP address/mask, destination address/mask, type of service, IP
protocol number.
TCP/UDP: Source port, destination port, and TCP flag.
Packet format.
For ACL details, see 2.8.6, “Access control lists” on page 97.
2.9.3 Summary of ACL actions
Actions determine how the traffic is treated. The VFSM QoS actions include the
following actions:
Pass or drop the packet.
Re-mark the packet with a new DiffServ Code Point (DSCP).
Get Implementing IBM System Networking 10Gb Ethernet Switches now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

