24 IBM Cognos Dynamic Cubes
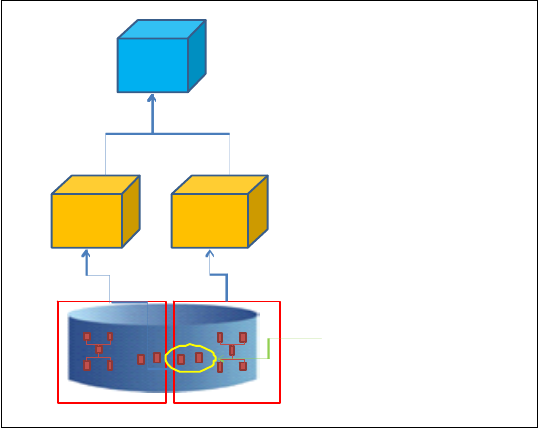
Figure 2-20 shows the availability of in-memory aggregates.
Figure 2-20 Availability of in-memory aggregates
2.2 Dynamic cubes and the Dynamic Query Mode server
Dynamic cubes are created within a DQM server. As such, an important concept to
understand is how dynamic cubes exist within a DQM server and how administrative
commands, metadata, and data requests are directed to a dynamic cube.This section
describes the interaction between a report server and a DQM server as it pertains to Cognos
Dynamic Cubes, the components of a dynamic cube within a DQM server, and finally, how
commands and requests are directed within the DQM server to a dynamic cube.
2.2.1 Dynamic cubes and report server
A dispatcher may host, at most, only a single DQM server, which appears as the
QueryService in the list of services associated with a dispatcher. All of the report servers that
run under a dispatcher communicate with the single DQM instance through a single port.
Thus, any dynamic cubes that are assigned to a dispatcher are all hosted within the single
instance of the DQM server.
It is possible to configure a cube on more than a single dispatcher, which can provide user
scalability. Note, however, that each instance of the DQM server hosts a separate version of a
cube. The interaction of a cube with the underlying relational database, and the management
of its caches, is distinct from that of any other instance of the cube on other dispatchers.
Consequently, distributing a cube, though it does allow for more users to access a single,
logical cube does incur some additional overhead:
Each computing node to which a dynamic cube is configured must have the memory and
CPU cores necessary to support the cube and its expected user volume, taking load
balancing into account.
If a dynamic cube is deployed across multiple nodes, the load on the underlying relational
database can be multiplied notably during the loading of in-memory aggregates if start,
restart, or data cache refresh operations are performed at the same time across the
multiple instances of the cube.
Sales Inve ntory
Sales
In ventory
Sum mary t able s availa ble
to base cube.
A base cube can construct
in-memory ag greg ate s f rom
data in fa ct t able .
A virtual cube has no direct access to
the data warehouse, so it cannot
access summary tables, or construct
in-memory aggre gat es
.
Get IBM Cognos Dynamic Cubes now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

