22 IBM Cognos Dynamic Cubes
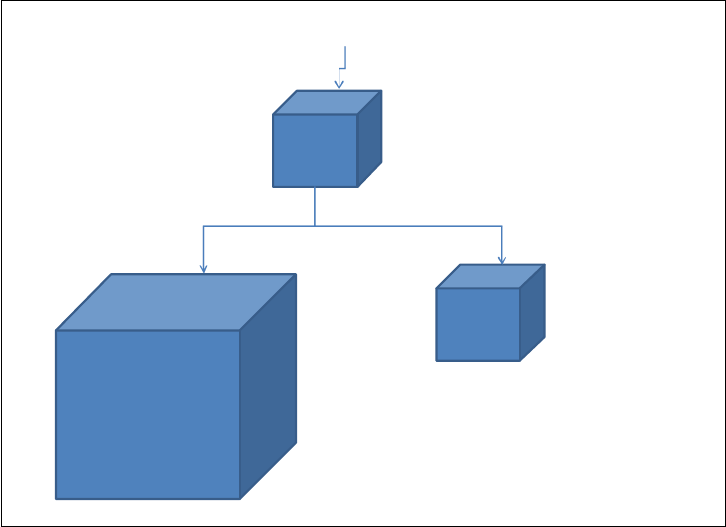
Figure 2-18 shows query decomposition with virtual cubes.
Figure 2-18 Query decomposition with virtual cubes
2.1.7 Aggregate Advisor
A key feature of Cognos Dynamic Cubes is its ability to take advantage of both in-database
and in-memory pre-computed summaries. These pre-computed summaries can improve the
performance of queries by orders of magnitude, providing the type of performance required
for interactive reporting and analysis.
If you have pre-existing summary tables in your data warehouse, you can model them as
aggregate cubes in the Cognos Cube Designer. When a cube is published and the cube is
restarted, it will automatically route SQL queries to the summary tables when possible. For
distributive measures (those whose aggregation rule is SUM, COUNT, MAX, or MIN),
summary tables can be employed to compute summary values at higher levels of aggregation
than that at which an aggregate cube is defined.
As useful as this capability is, one of the most difficult tasks when of pre-computed
summaries is trying to determine what it is that should be pre-aggregated, especially in a
large, multi-user environment that might involve hundreds or thousands of reports and
analyses. The Cognos Dynamic Cubes Aggregate Advisor, available as part of the Dynamic
Query Analyzer, performs this task.
The Aggregate Advisor can be used to suggest database aggregate tables, in-memory
aggregate cubes, or both. The Aggregate Advisor makes use of a cube’s model and statistics
it gathers from the underlying data warehouse to determine which summary tables to
suggest. However, it can also make use of workload log files that are generated from the
execution of reports and analyses to make more accurate suggestions of what will optimize
the performance of an application workload.
Virtual
Cube
[Sales] by Dates ([2011], [Jan 2012], [Feb 2012])
2012
Sales
Cube
Historic
Sales
Cube
[Sales] by [Jan 2012], [Feb 2012]
[Sales] by [2012]
Chapter 2. IBM Cognos Dynamic Cubes architecture 23
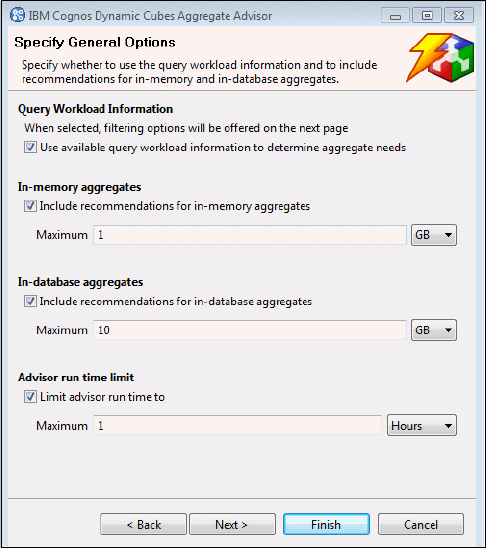
Figure 2-19 shows the Aggregate Advisor selection of workload information.
Figure 2-19 Aggregate Advisor selection of workload information
The workload log that is generated by the DQM server contains detailed information that can
be used as filters to isolate a subset of workload to be optimized. In addition, the information
in the workload log allows the Aggregate Advisor to determine which values to pre-aggregate
that can be used across a wide range of reports and analyses, for example, aggregating data
at the quarterly level and allowing this to be used to compute annual totals without
pre-computing the annual levels.
In-database aggregate suggestions contain a detailed description of each aggregation it
suggests, and a generic set of column descriptions and the database-specific SQL that can
be used to populate the table. These suggestions can be used by a DBA to construct the
necessary tables and the corresponding extract, transform, and load (ETL) scripts to build
and maintain the tables.
In-memory recommendations are published to CM. After a cube is restarted, the aggregates
execute the necessary SQL statements to retrieve the summarized values and place the
values in its aggregate cache for subsequent use during query processing.
Virtual cubes cannot have an aggregate cache because they have no underlying database
from which to obtain aggregate values.
Get IBM Cognos Dynamic Cubes now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

