Chapter 2. IBM Cognos Dynamic Cubes architecture 17
Figure 2-11 shows dynamic cube data access property.
Figure 2-11 Dynamic cube data access property
A dynamic cube also has a child model element that, if security is defined for a cube, contains
a collection of security views to which users, groups, or roles can be assigned.
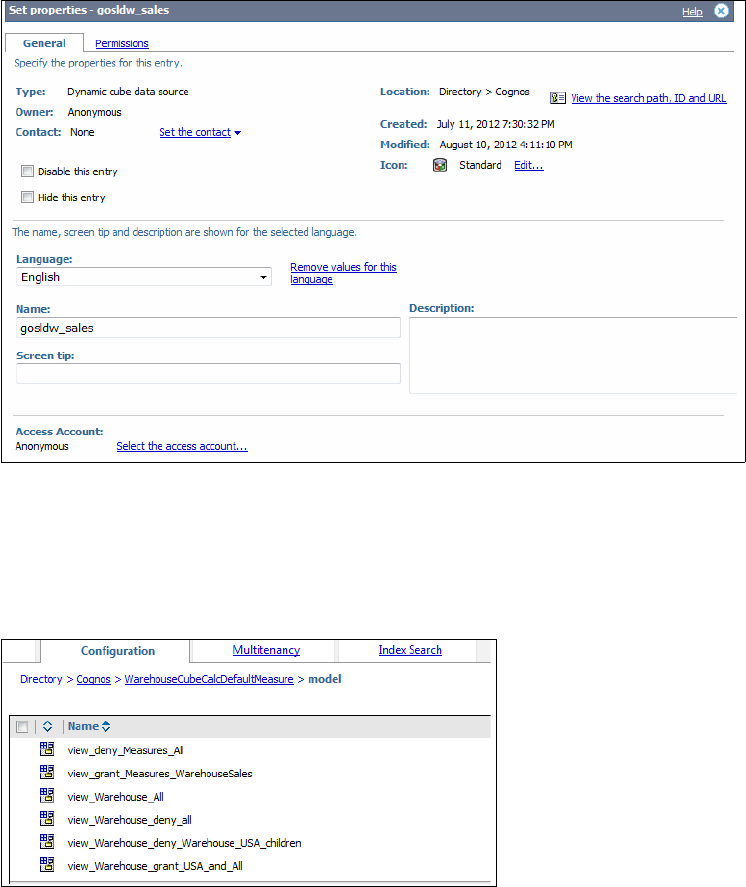
Figure 2-12 shows dynamic cube security views.
Figure 2-12 Dynamic Cube security views
By being presented in CM as a data source, a dynamic cube can be included in a Framework
Manager model as an OLAP data source, allowing it to be part of multidata source package.
2.1.4 Configuring dynamic cubes
Publishing a dynamic cube to CM as a data source does not make a cube suddenly
accessible to users. At this point, all that happened is that the metadata definition of a cube
was published so that it is accessible to other parts of Cognos. The next step to making a
cube available to users is to configure a dynamic cube for one or more dispatchers within a
Cognos installation. Configuring a dynamic cube for a dispatcher accomplishes two steps:
It identifies a specific dispatcher on which a cube can be active.
It defines the operational characteristics of a cube on that dispatcher.
18 IBM Cognos Dynamic Cubes
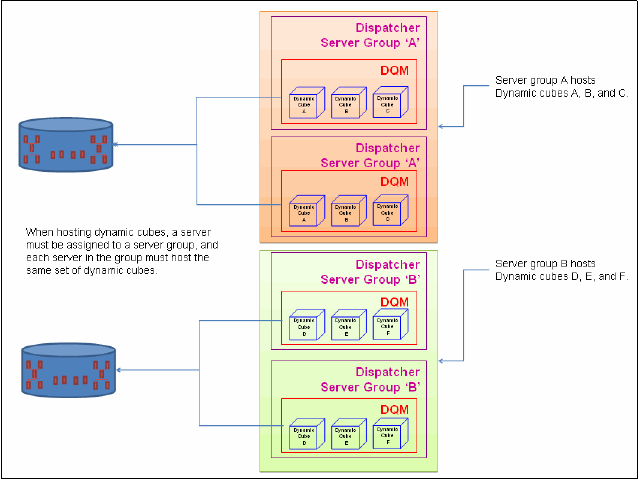
In most circumstances, dynamic cubes are assigned to specific dispatchers that are running
on hardware specifically allocated to house dynamic cubes because of their memory and
CPU requirements, which are in excess of what is normally required for a DQM server. One
consequence of this approach is the necessity to use advanced routing rules to route
requests for dynamic cubes to the appropriate dispatchers.
Figure 2-13 shows multiple cubes deployed across multiple servers.
Figure 2-13 Multiple cubes deployed across multiple servers
Each cube that is assigned to a dispatcher has its own set of properties. Several of the
properties, such as data and aggregate cache sizes, must be assigned non-default values
based on an evaluation of the data warehouse and the expected use of a cube. Other
properties may be assigned values during the course of the development and production
lifecycle of a cube, for example, the enabling of workload logging.
Because dynamic cubes are created within the DQM server, there are also QueryService
properties, notably those related to the JVM heap, that must be assigned values that take into
account the presence of dynamic cubes.
Get IBM Cognos Dynamic Cubes now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

