9Power Electronics in HEVs
9.1 Introduction
Power electronics is one of the enabling technologies propelling the shift from conventional gasoline/diesel engine‐powered vehicles to electric, hybrid, and fuel cell vehicles. This chapter discusses the power electronics used in HEVs and PHEVs. However, the focus of the chapter is on the unique aspects of power electronics in HEVs and PHEVs.
To explain the types of power electronics circuits used in an HEV, we use the configuration of a typical series HEV powertrain as shown in Figure 9.1. In this configuration, the internal combustion engine (ICE) drives a three‐phase permanent magnet synchronous generator, whose output is a three‐phase voltage with variable frequency and variable voltage. This output needs to be rectified to DC.
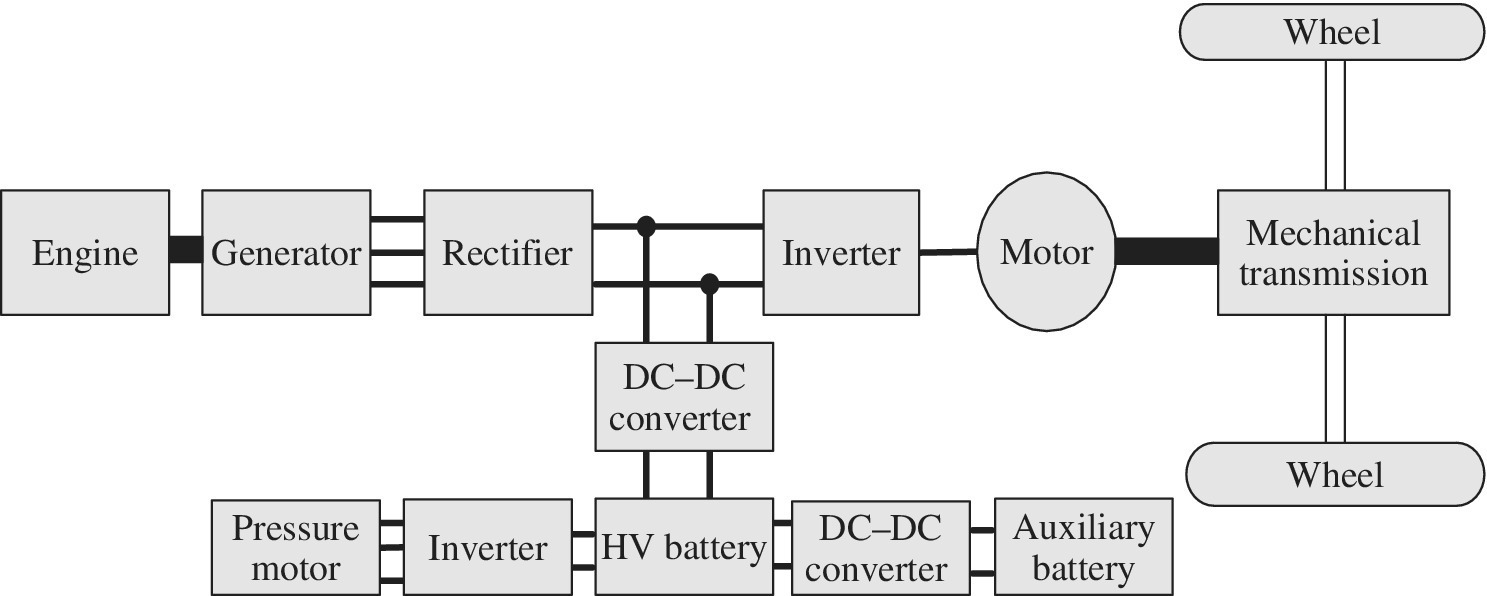
Figure 9.1 Power electronics converters used in a series HEV.
The front wheels are driven by an induction motor which needs to be controlled by a voltage source inverter (VSI) or a current source inverter (CSI). An energy storage system is connected to the DC bus, between the generator/rectifier output and the inverter. However, there is a bidirectional DC–DC converter that manages the charge/discharge of the battery, as well as controlling the DC bus voltage.
In conventional vehicles, the air‐conditioning (A/C) compressor is driven by the engine through a belt. In advanced HEVs, the engine is very often ...
Get Hybrid Electric Vehicles, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

