CHAPTER 7 Quantifying the Value of Information
- A
- B
- C
- C
- E
- True
- B
- A threshold is the exact value an uncertain variable on a continuum would have in order to break even on a decision. Below that value one choice is better and above that value another choice is better.
-
A
Threshold = 6 × X = 3,000,000
Solving for X, X = 500,000
Relative threshold = (500,000 – 300,000)/(800,000 – 300,000) = 0.4
EOLF (using EOLF chart) = 80
EVPI = EOLF/1,000 × OL per unit × (BB – WB) = 240,000
Or the spreadsheet for information value for normal distributions can be used to produce a value that should be close to the same.
- E
- A
- D
- True
- E
- C
- A
- B
- E
-
16%
Using the Excel function we write: =NORMDIST(85,100,15,1)
-
$20,000
EOL = .2 × $100,000 = $20,000
-
0.33
RT = (Threshold – WB)/(BB – WB)
=(6000 – 4000)/(10000 – 4000)
- Using either the EOLF chart or the information value for normal distributions, you should get an answer close to about $17,000 or so.
- A situation where demand is uncertain but the losses from overstocking are less than the losses for understocking by the same amount.
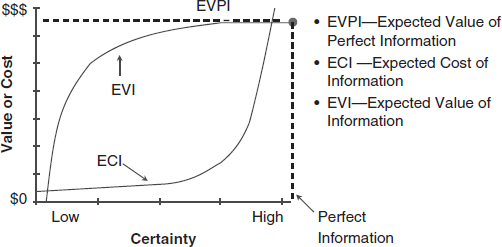
- Challenge:
- The discrete approximation starts with creating a table that divides the distribution into a large number of increments—perhaps hundreds or perhaps even one increment per unit of the product.
- For each increment, compute the probability of that increment given the 90% CI entered.
- For each increment, compute a loss of ...
Get How to Measure Anything Workbook: Finding the Value of Intangibles in Business now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

