1.4 Electronic Trading Revolution in FX Market
The electronic trading revolution in FX has transformed the market's structure while improving market quality in terms of transparency and transaction costs. This section describes this transformation, which proceeded in two stages. In the first, electronic trading platforms essentially replaced the telephone. In the second stage, market participants developed previously unanticipated ways to exploit the new technology.
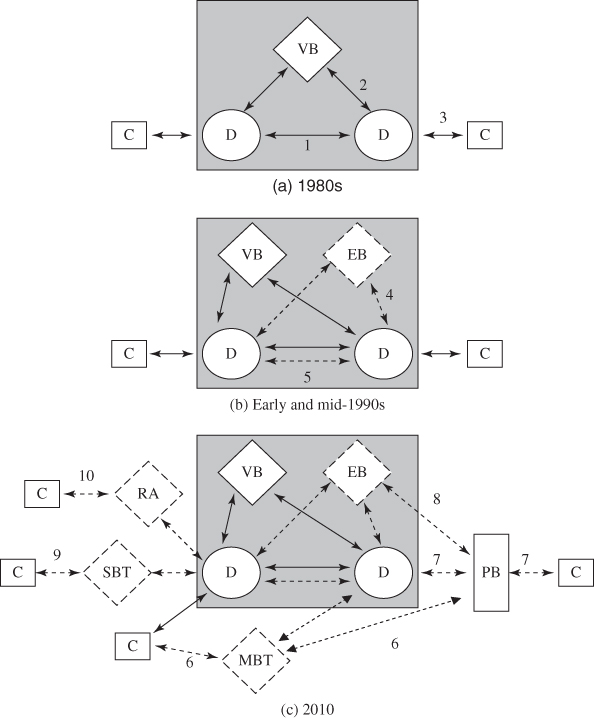
To help clarify the structures, Figure 1.3 provides a stylized depiction of the FX market structure at different points in time. In each frame, the interdealer market is represented by the shaded box and the customer market is the area outside the shaded box. Channels for transacting FX are numbered arrows. Solid lines represent voice channels for trading over the telephone; dotted lines represent electronic execution methods.
Figure 1.3 Evolution of FX market structure. Note: D, dealer; C, client; VB, voice broker; EB, electronic broker; PB, prime broker; MBT, multibank trading system; SBT, single-bank trading system; RA, retail aggregator. Solid lines represent voice execution methods. Dashed lines represent electronic execution methods.
1.4.1 The Telephone Era
Currency trading was a sleepy business before exchange rates began floating in the early 1970s. As the business took off, FX trading in the OTC market was ...
Get Handbook of Exchange Rates now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

