15-1. IEEE Format
We will restrict our attention to the single and double formats (32- and 64-bit) described in IEEE 754. The standard also describes “single extended” and “double extended” formats, but they are only loosely described because the details are implementation-dependent (e.g., the exponent width is unspecified in the standard). The single and double formats are shown below.
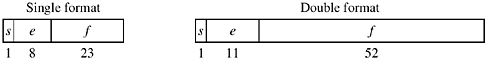
The sign bit s is encoded as 0 for plus, 1 for minus. The biased exponent e and fraction f are magnitudes with their most significant bits on the left. The floating-point value represented is encoded as shown on the next page.
As an example, consider encoding ...
Get Hacker's Delight now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

