2-3. Inequalities among Logical and Arithmetic Expressions
Inequalities among binary logical expressions whose values are interpreted as unsigned integers are nearly trivial to derive. Here are two examples:
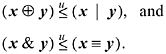
These can be derived from a list of all binary logical operations, shown in Table 2-1.
Let f(x, y) and g(x, y) represent two columns in Table 2-1. If for each row in which f(x, y) is 1, g(x, y) also is 1, then for all (x, y),
![]() Clearly, this extends to word-parallel logical operations. One can easily read off such relations (most of which are ...
Clearly, this extends to word-parallel logical operations. One can easily read off such relations (most of which are ...
Get Hacker's Delight now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

