2
Tensor Analysis and Riemannian Geometry
Part I Line Element
2.1 RIEMANNIAN SPACE
In the Euclidean space of three dimensions, each point is specified by three coordinates (x1, x2, x3). The distance ds between two neighbouring points (x1, x2, x3) and (x1 + dx1, x2 + dx2, x3 + dx3) is given by
We may extend the concept of Cartesian space in three dimensions to n-dimensional space. Each point will be designated by n coordinates (x1,x2,…,xn), which are shown collectively by (x). Further, we assume that the distance between any two neighbouring points is given by
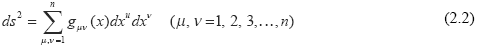
where gμν (x) are functions of the coordinates ...
Get General theory of Relativity now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

