Chapter 4. Core Games
ONCE YOU START PLAYING AND CREATING YOUR OWN GAMES, you will likely find a short list of activities that work well in any situation. These are the reliable techniques that never let you down. They’re simple enough to show up as “moves” in other games, making them a great place to start.
The 7Ps Framework
OBJECT OF PLAY
Every meeting deserves a plan. Note that a great plan can’t guarantee a great outcome, but it will help lay down the fundamentals from which you can adapt. Sketch out these fundamentals by using the 7Ps framework.
NUMBER OF PLAYERS
Individual
DURATION OF PLAY
20 minutes to 2 hours
HOW TO PLAY
Use these items as a checklist. When preparing for a meeting, thinking through the 7Ps can improve focus and results, even if you have only a few moments to reflect on them.
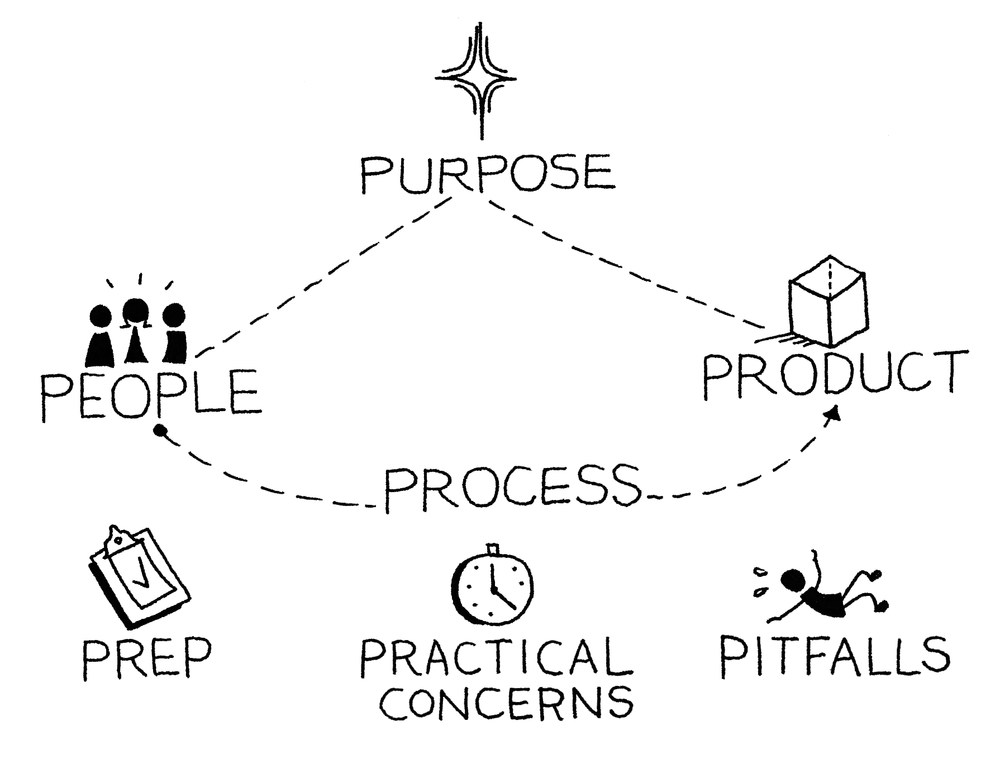
- Purpose:
Why are you having this meeting? As the leader, you need to be able to state this clearly and succinctly. Consider the urgency of the meeting: what’s going on, and what’s on fire? If this is difficult to articulate, ask yourself if a meeting is really necessary.
- Product:
What specific artifact will we produce out of the meeting? What will it do, and how will it support the purpose? If your meetings seem to be “all talk and no follow-through,” consider how a product might change things.
- People:
Who needs to be there, and what role will they play? One way to focus your list of attendees is to think in terms of questions and answers. What questions are we answering with this meeting? Who are the right people to answer the questions?
- Process:
What agenda will these people use to create the product? Of all the 7Ps, the agenda is where you have the most opportunity to collaborate in advance with the attendees. Co-design an agenda with them to ensure that they will show up and stay engaged.
- Pitfalls:
What are the risks in this meeting, and how will we address them? These could be as simple as ground rules, such as “no laptops,” or specific topics that are designated as out of scope.
- Prep:
What would be useful to do in advance? This could be material to read in advance, research to conduct, or “homework” to assign to the attendees.
- Practical Concerns:
These are the logistics of the meeting—the where and when, and importantly, who’s bringing lunch.
STRATEGY
Each of the 7Ps can influence or change one of the others, and developing a good plan will take this into account. For instance, if you have certain participants for only part of a meeting, this will change your process.
Get others involved in the design of the meeting. Their participation in its design is the quickest route to its effectiveness.
Recurring meetings can take on a life of their own and stray from their original purpose. It’s a healthy activity to revisit “Why are we having this meeting?” regularly for such events.
Make the 7Ps visible during the meeting. These reference points can help focus and refocus a group as needed.
Have a plan and expect it to change. The 7Ps can give you a framework for designing a meeting, but they can’t run the meeting for you. The unexpected will happen, and as a leader you will need to adapt.
The 7Ps Framework is credited to James Macanufo.
Affinity Map
OBJECT OF PLAY
Most of us are familiar with brainstorming—a method by which a group generates as many ideas around a topic as possible in a limited amount of time. Brainstorming works to get a high quantity of information on the table. But it begs the follow-up question of how to gather meaning from all the data. Using a simple Affinity Diagram technique can help us discover embedded patterns (and sometimes break old patterns) of thinking by sorting and clustering language-based information into relationships. It can also give us a sense of where most people’s thinking is focused. Use an affinity diagram when you want to find categories and meta-categories within a cluster of ideas and when you want to see which ideas are most common within the group.
NUMBER OF PLAYERS
Up to 20
DURATION OF PLAY
Depends on the number of players, but a maximum of 1.5 hours
HOW TO PLAY
On a sheet of flip-chart paper, write a question the players will respond to along with a visual that complements it. Conduct this game only when you have a question for the players that you know will generate at least 20 pieces of information to sort.
Ask each player to take 10 minutes to generate sticky notes in response to the question. Use index cards on a table if you have a group of four or less. Conduct this part of the process silently.
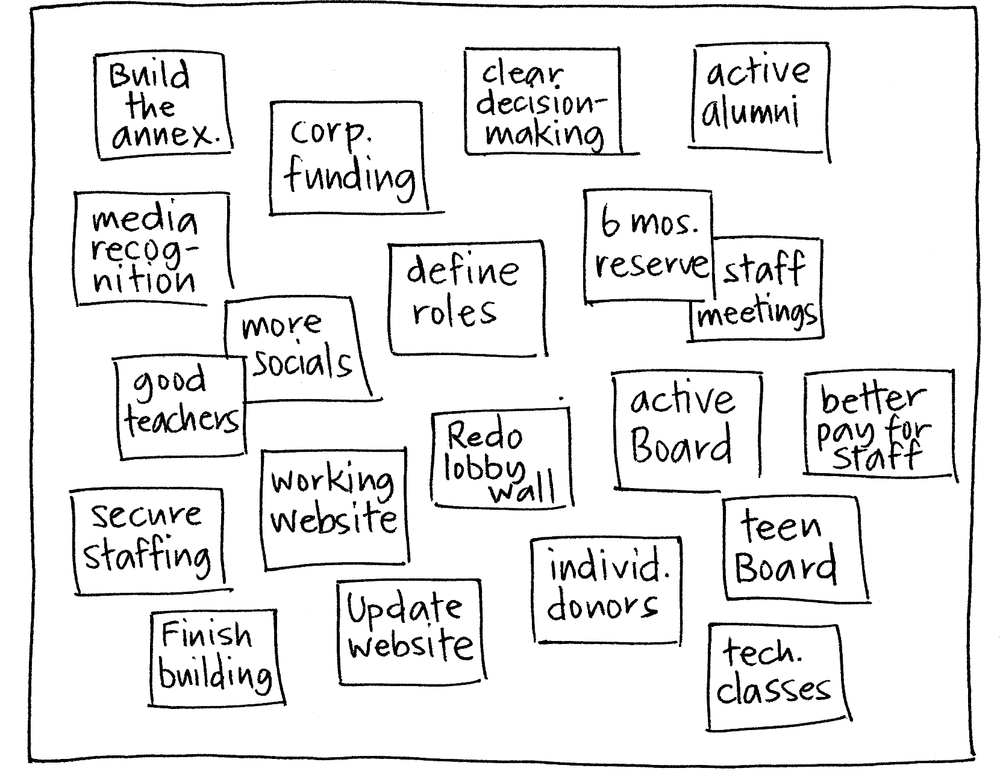
Collect the ideas from the group and post them on a flat working surface visible to everyone. It should end up resembling the following figure.
Based on guidance from the players, sort the ideas into columns (or clusters) based on relationships. Involve the group in the process as much as possible. Have the players approach the wall to post their notes—it saves time—and allow them to do an initial, general sorting in columns or clusters.
Create a sticky-note “parking lot” close to the display for ideas that don’t appear to fall into a natural category. Redundancy in ideas is OK; don’t discard sticky notes because they’re already represented. It’s helpful to leave repeated ideas posted since it indicates to the group how many people are thinking the same thing. At this stage, ask the players to try to avoid searching for higher categories and simply to focus on grouping the information based on the affinities.
Once the content is sorted, ask the group to suggest categories that represent the columns you’ve created and write the categories they agree on at the top of the column (or near a cluster if you chose a cluster rather than a column display). Don’t let the players spend an inordinate amount of time agreeing on a name for a category. If there’s disagreement over “Facilities” versus “Infrastructure,” write them both. If the players produce categories that are significantly different, pay attention to which category gets the most approval from the group and write that one. Your visual may end up looking like the one below.
STRATEGY
The value of the Affinity Diagram game increases when two conditions are met. The first is that the players generate multiple data points, ideally with good information. The second relates to the quality of the sorting. The cleaner the players’ insights when they form relationships within the content, the better the categories will be.
Note
Fun, optional activity: Run through the Affinity Diagram game once, complete with categorizations. Then ask the group to reshuffle the sticky notes and recombine the ideas based on affinities they didn’t notice in the first round.
Sometimes affinities within content are crystal clear, so the sorting becomes less pivotal, but when those relationships are more nuanced, it’s more important that the sorting process is done well. In a situation in which there are many ways to affinitize information, assume a stronger facilitative role. Ask questions about the columns or clusters to clarify the group’s thinking and steer them toward an appropriate number of categories. If there are too many, the data gets watered down. If there are too few, the analysis gets watered down. Help the players find the sweet spot.
The affinity diagram was devised by Jiro Kawakita in the 1960s. It is also referred to as the KJ Method.
Bodystorming
OBJECT OF PLAY
Bodystorming is simply brainstorming, but done with the body. It may look different depending on the preparations and location, but in the end all bodystorming is fundamentally about one thing: getting people to figure things out by trying things out.
A group may explore one of the techniques described below to get their feet wet with bodystorming. They may move through them in order, from observing and learning to ideation and prototyping, although this is not a strict sequence. Each level of bodystorming will help break the pattern of analyzing ideas around a conference table and get people closer to developing things that will work in the real world.
HOW TO PLAY
Bodystorming takes place in three phases.
Level 1: Go Observe
Go to the location to do your work. If you are developing an idea for a coffee shop, or a shopping mall, or a hospital, go there and do your work as you would normally. The environment will present idea cues and authentic information that would never emerge from conference room brainstorming.
For example, say a group is charged with improving the student experience on a college campus. Although they may conduct interviews or other research, they may start by going to a few campus locations and “blending in” with the surroundings while going about their usual work. It’s important that the group not zero in on any specific analysis so that they will be open to the cues that the environment presents.
Level 2: Try It Out
Use role play and props to develop an idea. In this exercise, a group physically “acts out” an experience by using whatever they have on hand or can acquire. The group focuses on how they interact with each other, their surroundings, and makeshift artifacts, testing existing ideas and uncovering new ones.
For example, say a small group is asked to “reimagine the evening news.” Using each other as the actors, the audience, the news anchors, and the television itself, they improvise a script that plays out the experience as they conceive it could be.
Identify and assign critical roles. For any experience, identifying the “customer” or “user” role is a good way to get started. This participant (or group of participants) becomes the focal point and main character of the bodystorm.
Other critical roles will present themselves. “Who wants to be the Internet?” is not an uncommon question to hear.
Improvise the experience. Bodystorming is physical and progressive: as the group starts to put their thoughts into action, they will naturally ask simple and important questions by acting them out, often leading to the unexpected. For example, in the evening news scenario:
“OK, so how do you watch the evening news?”
“I don’t have a television. Also, I’m usually out jogging.”
“Oh. Do you have your phone on you?”
“Always. I’m listening to music.”
“OK, what if this happened... who wants to play the phone?”
In a completely improvised scenario, the group should keep in mind the principal rule of the game: building on each other’s inputs. “Yes, and...” will generate more progress than “Yeah, but...” thinking.
In some uses of bodystorming, a group will act out a script prepared in advance. In these cases, an equal amount of planning in props to build an environment is key. For example, if it’s a coffee shop, set up the counter and chairs. If it’s a park or outdoor area, strongly consider going there.
Level 3: Reflect on What Happens, and Why
By enacting the experience, the participants will naturally explore new possibilities, and uncover flaws or assumptions about how an idea could work. This is valuable both in the process itself and afterward: by documenting the exercise on video, the participants may later “watch the reel” to discuss key points.
STRATEGY
Choose the right level of bodystorming at the right time for the group. Because bodystorming asks participants to take a big step away from the typical conference table mode of thinking, they may need to get comfortable with more structured sessions first, armed with scripts and specific roles, before stepping into complete improv. In all cases, the exercise itself will be more memorable than the customary problem-solving session, and will help generate empathy that comes from “embodying” the experience.
The term “bodystorming” was coined by Colin Burns at CHI ’94 In Boston, Massachusetts.
Card Sort
OBJECT OF PLAY
Card sorting is a practice used frequently by information architects and designers to gather and structure inputs for a variety of purposes. In a common use of card sorting, information for a website is put onto the cards, and the sorting helps create categories for navigation and the overall architecture. The method works just as well for creating slides for presentations, or at any point where information needs to be sorted and organized in a sensible way.
The applications of card sorting are numerous, and in use it works similarly to Post-Up and affinity mapping. Card sorting can differ from these methods, however. First, the cards are generally prepared in advance, although participants should be allowed to create their own while sorting. Second, the cards are a semi-permanent artifact and can be used as a control over several exercises with different participants to find patterns among them.
NUMBER OF PLAYERS
Small groups or individuals
DURATION OF PLAY
30 minutes or more, depending on the number of cards and participants
HOW TO PLAY
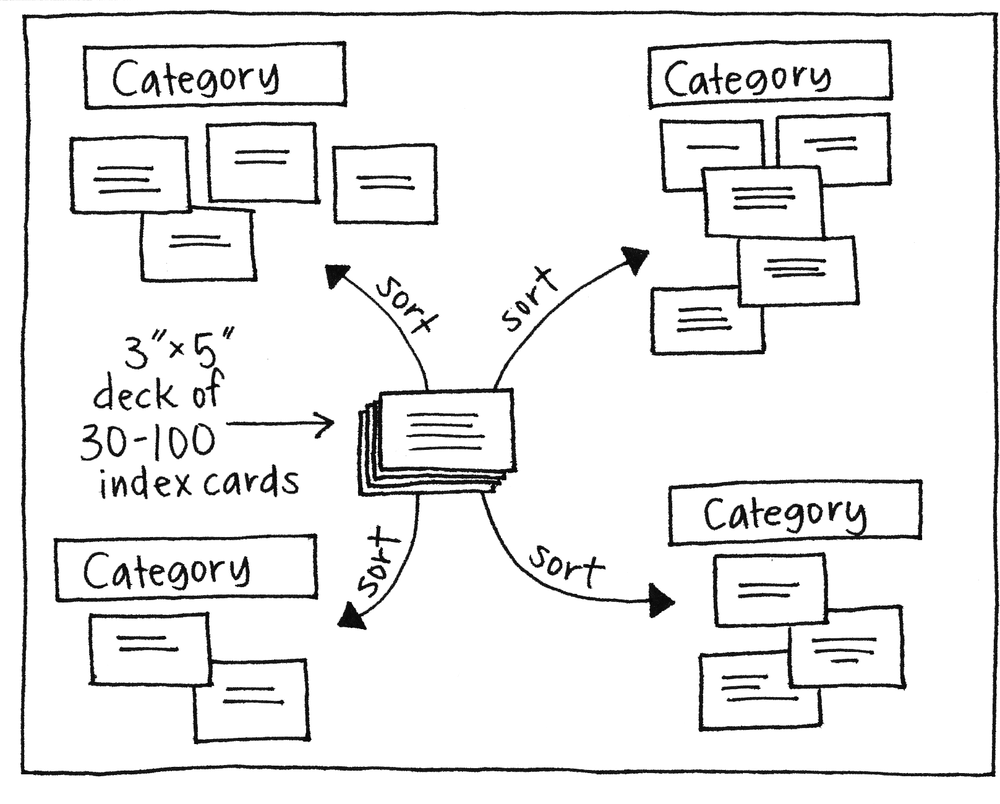
Use 3×5 index cards or similar. For a typical sorting exercise, aim for 30–100 cards in total; more than this range will likely overwhelm the participants, and fewer may not be meaningful enough to be worth the effort.
On each card should be a succinct bit of information; enough to tell the participants what it is and no more. Putting too much information on a card will slow down the sorting; not enough will cause confusion and will slow down the process even more.
Give the group the shuffled deck and a stack of blank cards. Describe the overall organization challenge, and ask them to sort the cards into groups that go together. If they think something is unclear or missing, they may alter a card or create a new one. Once they have created the groups, ask them to name them and describe them.
There are variations of sorting—including asking the group to rank the items from most to least desirable or to organize the cards into two categories such as “must have” and “nice to have.” You may also ask the group to sort cards into a predefined set of categories, to test their validity.
STRATEGY
Although the Card Sort game won’t tell you everything you need to know about a set of information, it will help reveal the thought process of participants. In this sense, it’s more about people than information. Only after a number of sorting exercises with a number of groups will larger patterns appear.
Card sorting is a common practice of information architects and designers of complex systems. Its actual source is unknown.
Dot Voting
OBJECT OF PLAY
In any good brainstorming session, there will come a time when there are too many good ideas, too many concepts, and too many possibilities to proceed. When this time has come, dot voting is one of the simplest ways to prioritize and converge upon an agreed solution.
NUMBER OF PLAYERS
At least 3 participants; in larger groups, tallying votes will be more time-consuming
DURATION OF PLAY
Short
HOW TO PLAY
First, the group needs a set of things to vote on! This may be something they have just developed, such as a wall of sticky notes, or it may be a flip-chart list that captures the ideas in one place. Ask the group to cast their votes by placing a dot next to the items they feel the most strongly about. They may use stickers or markers to do this. As a rule of thumb, giving each participant five votes to cast works well.
Participants cast their votes all at once and they may vote more than once for a single item if they feel strongly about it. Once all the votes are cast, tally them, and if necessary make a list of the items by their new rank.
This prioritized list becomes the subject of discussion and decision making. In some cases, it may be useful to reflect on ideas that didn’t receive votes to verify that they haven’t been left behind without cause.
STRATEGY
This technique is used to collaboratively prioritize any set of items. It could be used to hone a list of features, to agree on discussion topics, or to choose among strategies and concepts. Giving participants five votes is enough to be meaningful while still asking for individual prioritization; however, this is not a hard rule.
The original source of the Dot Voting game is unknown.
Empathy Map
NUMBER OF PLAYERS
3–10
DURATION OF PLAY
10–15 minutes
HOW TO PLAY
Personas help focus a group’s attention on the people involved in a project—often the customer or end user. Although creating an empathy map is not the rigorous, research-based process that is required for developing personas, it can quickly get a group to focus on the most important element: people.
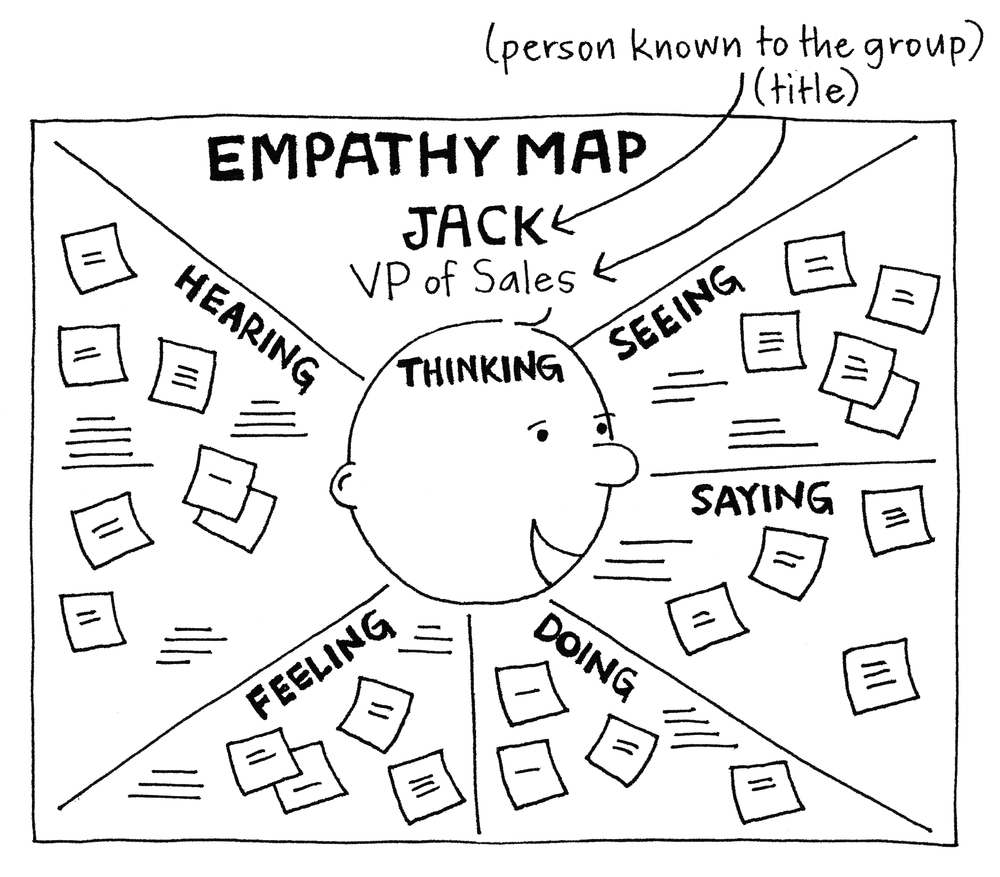
In this exercise, you will be creating a study of a person with the group. Start by drawing a large circle that will accommodate writing inside. Add eyes and ears to make it into a large “head.”
Ask the group to give this person a name.
Label large areas around the head: “Thinking”, “Seeing”, “Hearing”, and “Feeling”.
Ask the group to describe—from this person’s point of view—what this person’s experience is, moving through the categories from seeing through feeling.
The goal of the exercise is to create a degree of empathy for the person with the group. The exercise shouldn’t take more than 15 minutes. Ask the group to synthesize: What does this person want? What forces are motivating this person? What can we do for this person?
STRATEGY
The group should feel comfortable “checking” each other by referring back to the empathy map. When this happens, it will sound like “What would so-and-so think?” It’s good to keep the empathy map up and visible during the course of the work to be used as this kind of focusing device.
The Empathy Map game was developed by Scott Matthews of XPLANE.
Forced Ranking
OBJECT OF PLAY
When prioritizing, a group may need to agree on a single, ranked list of items. Forced ranking obligates the group to make difficult decisions, and each item is ranked relative to the others. This is an important step in making decisions on items like investments, business priorities, and features or requirements—wherever a clear, prioritized list is needed.
NUMBER OF PLAYERS
Small group of 3–10 participants
DURATION OF PLAY
Medium to long; 30 minutes to 1 hour depending on the length of the list, the criteria, and the size of the group
HOW TO PLAY
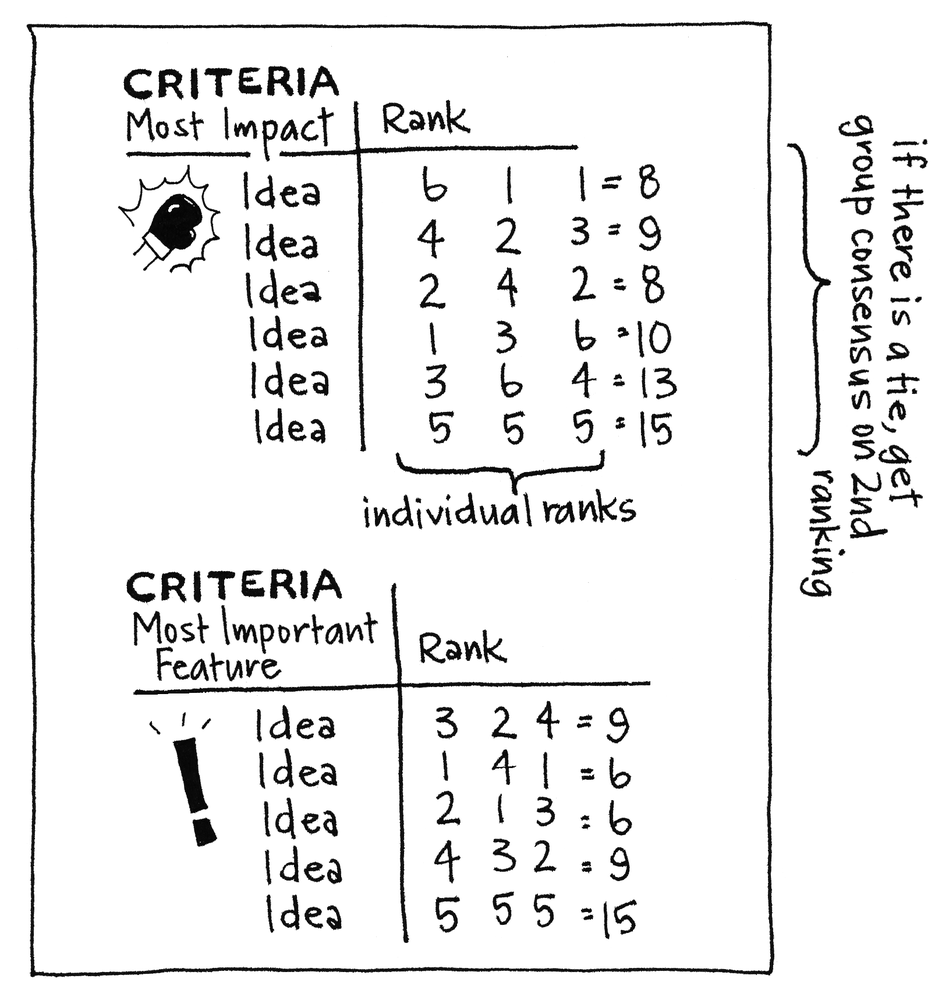
To set up the game, participants need to have two things: an unranked list of items and the criteria for ranking them. Because forced ranking makes the group judge items closely, the criteria should be as clear as possible. For example, in ranking features for a product, the criteria might be “Most important features for User X.” In the case of developing business priorities, the criteria might be “Most potential impact over the next year.”
If there are multiple dimensions to a ranking, it is best to rank the items separately for each criterion, and then combine the scores to determine the final ranking. It is difficult for participants to weigh more than one criterion at a time, as in the confusing “Most potential impact over the next year and least amount of effort over the next six months.” In this case, it would be best to rank items twice: once by impact and once by effort.
Although there is no hard limit on the number of items to be ranked, in a small-group setting the ideal length of a list is about 10 items. This allows participants to judge items relative to one another without becoming overwhelming. By making the entire list visible on a flip chart or whiteboard, participants will have an easier time ranking a larger list.
To play, create a matrix of items and the criteria. Each participant ranks the items by assigning it a number, with the most important item being #1, the second most important item as #2, and so forth, to the least important item. Because the ranking is “forced,” no items can receive equal weight.
Once the items have been ranked, tally them and discuss the prioritized list and next steps.
STRATEGY
Creating a forced ranking may be difficult for participants, as it requires they make clear-cut assessments about a set of items. In many cases, this is not the normal mode of operation for groups, where it is easier to add items to lists to string together agreement and support. Getting people to make these assessments, guided by clear criteria, is the entire point of forced ranking.
The original source of the Forced Ranking game is unknown.
Post-Up
NUMBER OF PLAYERS
1–50
DURATION OF PLAY
10 minutes to 1 hour
HOW TO PLAY
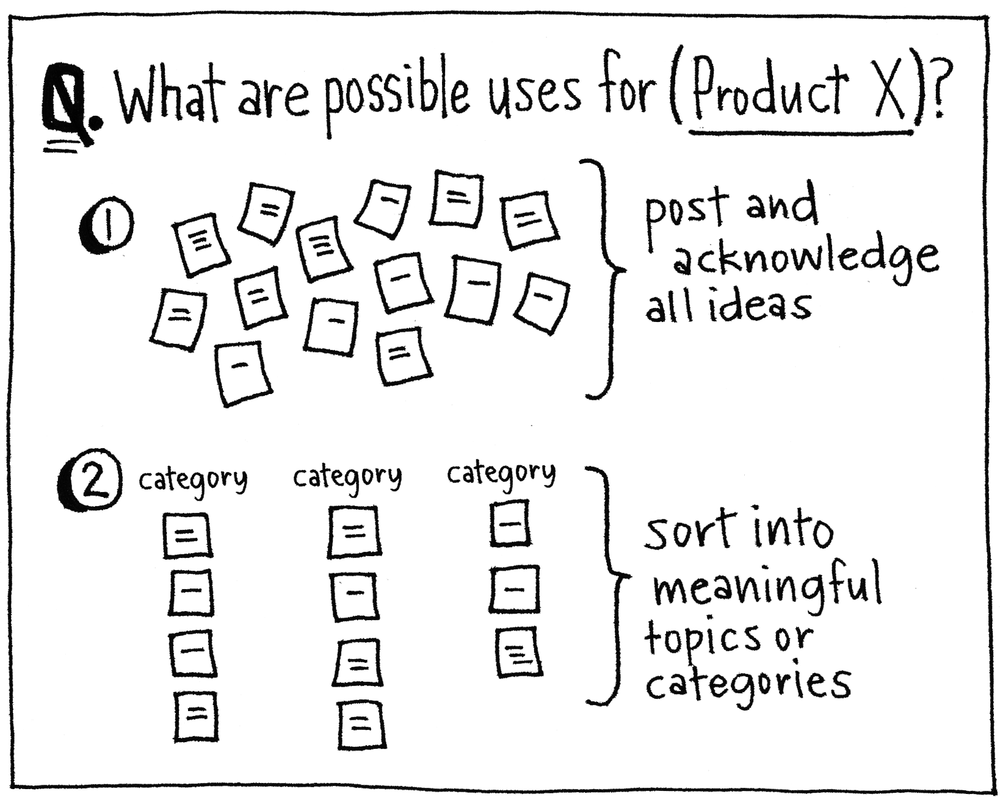
There are many ways to work with ideas using sticky notes. Generating ideas is the most basic play, and it starts with a question that your group will be brainstorming answers to. For example: “What are possible uses for Product X?”
Write the question or topic on a whiteboard. Ask the group to brainstorm answers individually, silently writing their ideas on separate sticky notes. The silence lets people think without interruption, and putting items on separate notes ensures that they can later be shuffled and sorted as distinct thoughts. After a set amount of time, ask the members of the group to stick their notes to the whiteboard and quickly present them.
If anyone’s items inspire others to write more, they can stick those up on the wall too, after everyone has presented.
STRATEGY
Generating ideas is an opening activity, and a first step. From here you can create an affinity map or a bottom-up tree, or further organize and prioritize the thoughts.
The Post-Up game is based on the exercises in Rapid Problem-Solving with Post-it® Notes by David Straker.
Storyboard
OBJECT OF PLAY
This game asks players to envision and describe an ideal future in sequence using words and pictures. Storyboarding as a technique is so versatile that it can be used to show any topic, not just an ideal future. But it is particularly powerful as a visioning exercise since it allows players to imagine and create possibilities. The players tell a story with a happy ending, planting tiny seeds for a different future. You can also use storyboarding to let employees describe their experience on a project, to show approaches to solving a problem, or to orient new employees on policies and procedures—its uses are limited only by the imagination.
NUMBER OF PLAYERS
8–20
DURATION OF PLAY
45 minutes to 1.5 hours
HOW TO PLAY
Before the meeting, determine the topic around which the players will craft their “ideal” story. Once the meeting starts, divide the group into pairs or groups of three or four, depending on the size of the group. Provide markers, pads of flip-chart paper, and stands.
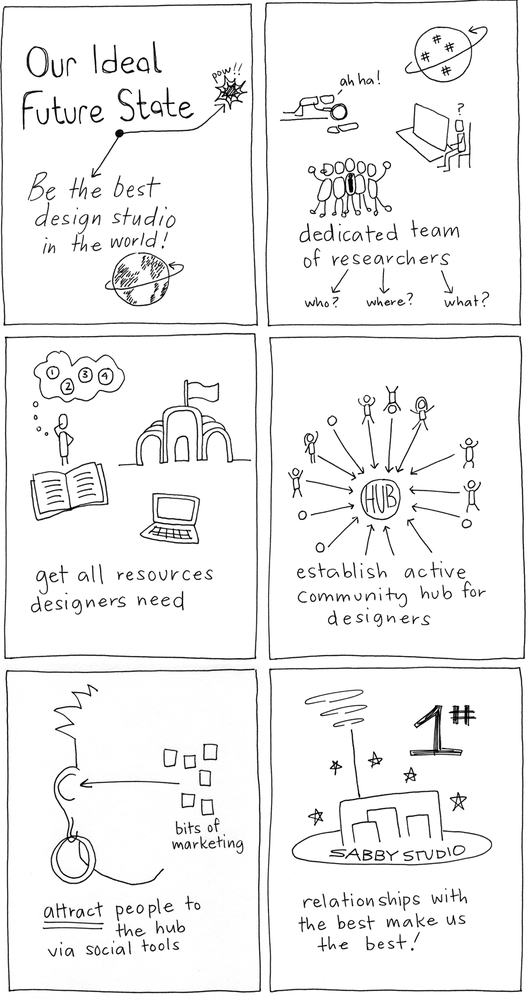
Tell the players that the purpose of this game is to tell the other players a feel-good story. The topic of the story is “The Ideal Future for [blank]”—for a team, a product, the company, whatever you decided beforehand. The players’ assignment is to visually describe the topic and narrate it to the group.
After the groups are established, give them 20–25 minutes to (1) agree on an ideal state, (2) determine what steps they would take to get there, and (3) draw each step as a sequence of large images or scenes, one per sheet of flip-chart paper.
Give the players a two-minute time warning, and once the time is up, bring them back together. Ask for volunteers to tell the story first.
After all the groups have presented, ask them what’s inspiring in what they heard. Summarize any recurring themes and ask for observations, insights, and “aha’s” about the stories.
STRATEGY
As the leader of this game, be sensitive to the fact that many of the meeting participants will freak when you tell them that large-scale drawing is involved. Reassure them that the story is the point of the exercise and that the images play a supporting role. They can use words as captions to clarify the images and they can also select the “artist” within their group so that not everyone has to put marker to paper. (But it’s more fun for those who do.) Finally, remind them that they aren’t allotted sufficient time to create a da Vinci anyway, so stick figures work perfectly well.
For the presentation format, there are various options. Breakout groups can post each sheet of flip-chart paper in a row around the room and walk along the row as they tell the story. They can also leave the flip-chart pad intact and flip the pages over the stand as they narrate. They could choose to hang the sheets in rows and cover them, using one group member to act as a “Vanna White” and create a series of voilà moments. Tell them to have fun with it—they aren’t being graded on their stories (although you could make it a contest if it’s that kind of crowd). The process of creating and sharing the stories is what matters.
Walt Disney is credited for this activity. His need to animate Steamboat Willie in 1928 led to the process of storyboarding—a story told in sequence on a wall covered with a special kind of board. He found it to be an effective way to track progress and improve a story.
WhoDo
NUMBER OF PLAYERS
1–10
DURATION OF PLAY
20–45 minutes
HOW TO PLAY
Who do you want to do what? Almost any endeavor of substantial impact requires seeking help from others. Developing a WHO + DO list is a simple way to scope out the undertaking.
Start with the vision. Write out or visualize the big goal.
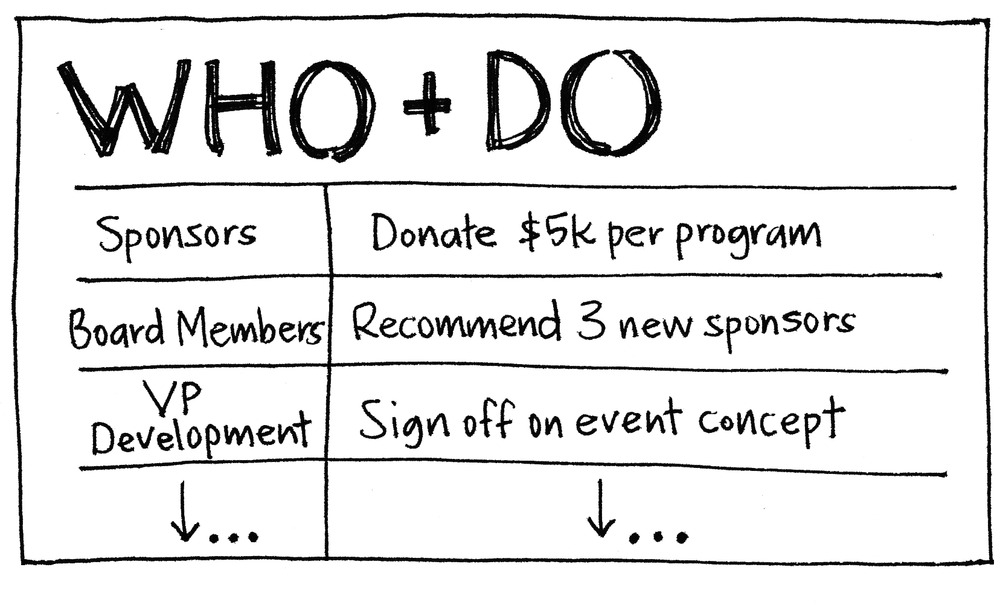
Draw a two-column matrix and write “WHO” on the left and “DO” on the right.
Ask: Who is involved in making this happen? Who is the decision maker? Who has needed resources? Who may be an obstacle? Whose support is needed? These individuals or groups are your list of WHOs.
The DOs are often harder. For each WHO, ask: What do they need to do, or do differently? What actions will build toward the big goal? Sharpen each WHO in the list until you have a desired and measurable action for each.
Given all of the possible WHOs and DOs, which are the most important? Who comes first?
STRATEGY
Bias yourself toward action. When brainstorming DOs, there is a tendency to slip into the easier mode of “we just want them to understand.” Most often when you want people to understand something, it’s because you want them to change something or learn something that they can then “DO.” Ask yourself, or the group, “What will happen once they understand?” Don’t shortchange what you are really looking for: action.
The WhoDo game is credited to Dave Gray.
Get Gamestorming now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.