Solving for implied volatility
Next we'll use a method for solving for implied volatility for European options. This can be done by numerically solving for the root using the bisection method.
To be able to understand why we use the bisection solver to find the root of the Black-Scholes equation, we need some tools. First we recapture the definition of the call and put price as a function of the estimated volatility and a set of parameters (denoted):
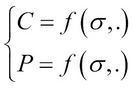
To extract the implied volatility, we need an inverse function of the Black-Scholes formula. Unfortunately, there is no analytical inverse of that function. Instead, we can say that the Black-Scholes ...
Get F# for Quantitative Finance now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

