Configuring Aging and Scavenging
Aging and scavenging is disabled by default since its improper use is dangerous. If you set the refresh and no-refresh intervals too low, records that aren’t stale can be inadvertently removed. A global setting controls aging and scavenging for the entire DNS server. It’s located on the Advanced tab of the server properties window, which is shown in Figure 7-7. The Scavenging period setting controls how often the server makes a scavenging pass through all authoritative zones.
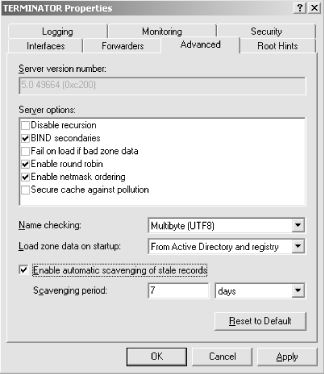 |
Once aging and scavenging has been enabled on a given server, you must still enable it for a particular zone. From the General tab of a zone’s properties window, click the Aging button to produce a window like the one shown in Figure 7-8. Click Scavenge stale resource records to enable aging and scavenging for this zone. The refresh and no-refresh intervals are set on a per-zone basis.
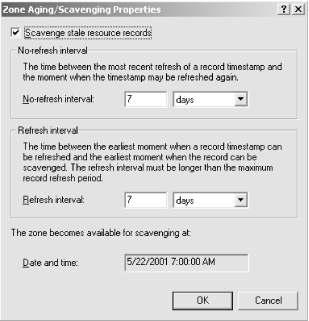 |
In addition, a DNS server may be configured to apply the zone’s values to all the existing and future zones.
Get DNS on Windows Server 2003, 3rd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

