Windows NT 4.0
In Windows NT, LAN resolver configuration is done from a single panel that looks remarkably similar to Windows 95’s, since NT 4.0 incorporated the Windows 95 “shell.” In fact, other than the presence of the new Edit button and the handy little arrows that allow you to reorder name servers and elements of the search list, there’s really no semantic difference between them, as shown in Figure 6-12.
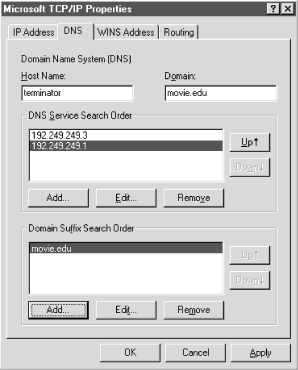 |
To get to the DNS Configuration panel, go to the Control Panel, click on Network, and select the Protocols tab. Double-click on TCP/IP Protocol, then select the DNS tab.
Windows NT also allows users to configure resolver settings specific to particular dial-up networking connections. To configure these, click on the My Computer icon, select Dial-Up Networking, pull down the top selection box, and choose the name of the DUN connection whose resolver you’d like to configure. Then click on the More pull-down and select Edit Entry then Modem Properties. Select the Server tab on the resulting window, and click on the TCP/IP Settings button. You’ll see the same window you’d see in Windows 95 (shown earlier).
If you leave the Server assigned name server addresses radio button checked, the resolver retrieves the name servers it should query from the server you dial into. If you check Specify name server addresses and specify the addresses ...
Get DNS on Windows Server 2003, 3rd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

