
Chapter 1. Business Intelligence overview 5
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), which has to do with managing the
bread-and-butter processes of an organization from planning, manufacturing,
inventory, shipping/distribution, accounting and human resources.
Workgroup collaboration, which has to do with sharing of resources and
information amongst an organizations employees such as E-mail, meetings,
document sharing, etc. Field Force Automation improves the productivity of
employees in the field (salesman, technical support/maintenance persons,
and delivery personnel) and improves customer satisfaction and
responsiveness.
Business Intelligence (BI) which has to do with collecting and analyzing
business information from a multitude of internal and external sources
for competitive advantage.
Knowledge Management (KM), which has to do with combining and matching
information and personnel skills to great effect.
By extending the reach of an organization's business critical systems using
Internet technologies, the opportunity exists to gain significant competitive
advantage by transforming:
Employees — from competent to responsive individuals
Customers — from one time interaction to lifetime loyalty through mass
personalization instead of mass marketing
Suppliers and distributors — from independence to interdependence
1.1.1 Impact of e-business
IT organizations have long understood their mission to support the applications
required to meet business objectives via an infrastructure that delivers
acceptable performance, availability, security, integrity and access to its user
community. Most business organizations today have successfully implemented
such infrastructures on private networks for their user community consisting of
primarily their worldwide employees.
However, e-business results in the addition of customers, suppliers and
distributors to the user community mix over the Internet, as well as intranets and
extranets, accessing business critical systems. This is because the user
community is now potentially global (requiring 7x24 operation), multi-lingual,
Important: When an organization connects its business critical systems
directly to customers, suppliers, distributors and employees in order to gain a
competitive advantage, it transforms the organization and becomes an
e-business.
6 High-Function Business Intelligence in e-business
generally use a browser interface on a multiplicity of client platforms, have a lot of
concerns over security and privacy, and can generate unpredictable workloads.
Customers in particular have choices (they are just a mouse-click away from
going over to the competition) and expect rapid response and superior service.
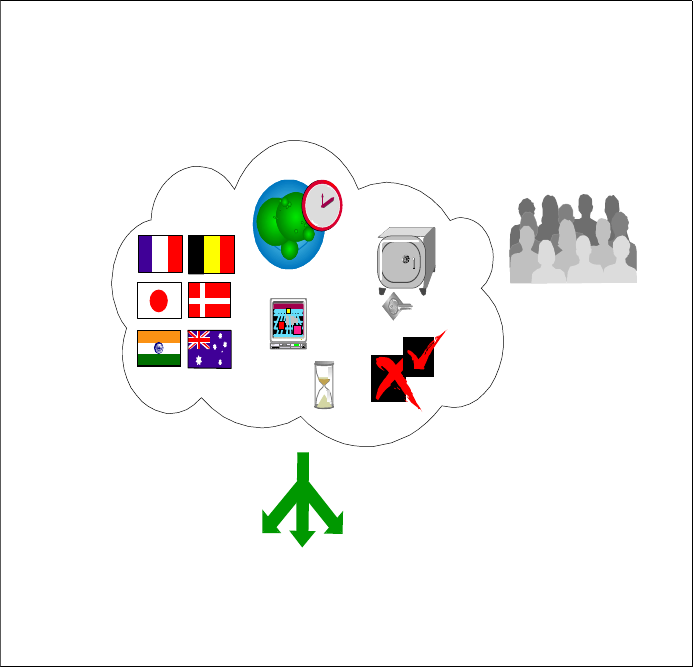
Figure 1-3 e-business impact
This has the potential to add orders of magnitude of complexity to the challenges
of managing the demands of the exploding user community. e-business
therefore exacerbates an already challenging situation.
e-business Impact
1
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Available (7x24)
We b
Enable
Scaleable
Secure
National
Language
Support
Connect
to
Busi ness
Criti cal
Systems
Support
Assorted
Client
Devices
Get DB2 UDB's High-Function Business Intelligence in e-business now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

