2 High-Function Business Intelligence in e-business
1.1 e-business drivers
A number of factors have changed the business environment in recent years —
from events such as global economics and competition, mergers and
acquisitions, and savvy and demanding customers — to technology advances
such as the World Wide Web, cheaper PCs and a host of Internet access devices
such as PDAs, cellular telephones, and set tops. This is shown in Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1 Changing business environment
Organizations clearly recognize that they can no longer dictate systems or
clients, that the Internet cannot be controlled, and that downtime will impact more
than employee productivity.
Events
Business
Global economics and competition
Mergers and acquisitions
Savvy customers
Technology
World Wide Web
Cheaper PCs
Internet access devices such as
PDA, palm, set top, telephone, etc.
Compressed time cycles from product conception to market
Customer Relationship Management
Reduce costs by streamlining processes
Exploit emerging opportunities
Changing Business Environment

Chapter 1. Business Intelligence overview 3
To survive and thrive in such an environment, organizations must adapt and
innovate — business as usual could be a recipe for disaster. More so than ever
before, the following issues are critical. It is now mandatory for a business to:
Acquire and retain loyal and profitable customers. Businesses must become
more responsive to its customers needs.
Reduce costs by streamlining and transforming business processes,
improving the productivity and efficiency of its employees and business
partners and customers (self service and cutting out the intermediary — or
disintermediation, as it is now called — is an important element here). While
reducing costs is a perennial favorite that is generally characterized by stop
and starts, this now takes on a new urgency.
Become competitive with very short product conception to implementation to
return on investment (ROI) cycles.
Pursue every possible channel such as the Internet, and exploit emerging
opportunities to ensure success and avoid failure.
Businesses recognize the urgency to transform various business processes for
competitive advantage.
Note: With government bodies, the emphasis is more on keeping its
constituents happy — since acquisition and attrition are not relevant in
most cases.
4 High-Function Business Intelligence in e-business
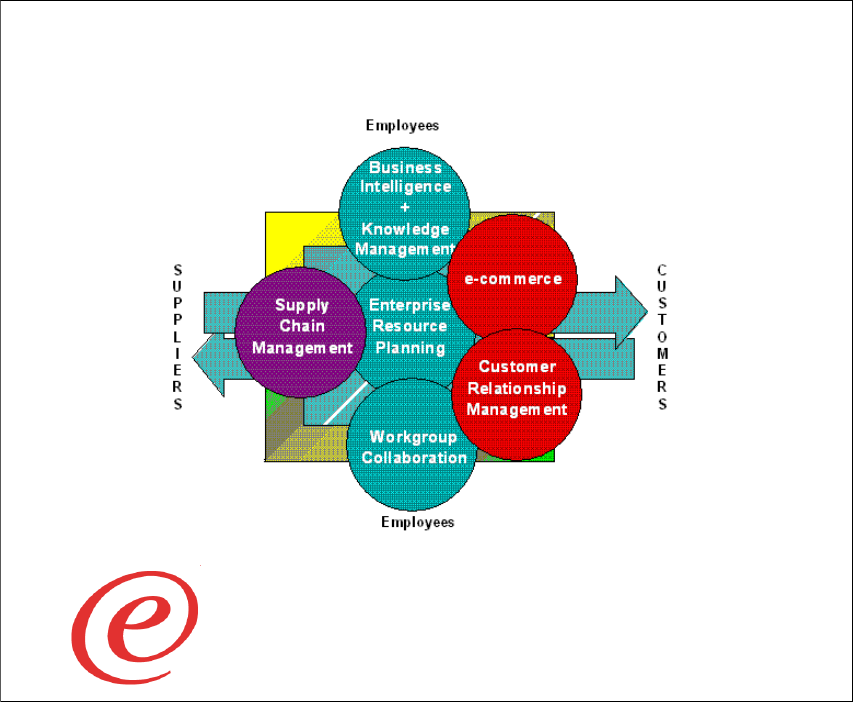
These processes are highlighted in Figure 1-2.
Figure 1-2 Business critical processes
These are the business critical processes we are concerned with:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM), which has to do with identifying,
understanding, anticipating and satisfying customer needs, that is, building
loyalty through improved customer satisfaction.
e-commerce, which is a new channel for an organization's goods and
services to a whole wider global market.
Supply Chain Management (SCM), which has to do with inter-company
business processes. This involves improving the efficiency (and reducing
costs) of interactions with suppliers, partners, distributors, customers, etc.
Business Critical Processes
An e-business organization connects critical business systems
directly to employees, customers, suppliers and distributors, via the
internet, intranets and extranets to gain a competitive advantage
Get DB2 UDB's High-Function Business Intelligence in e-business now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

