10.2 Spectral Models
The most common approach for converting a time-domain signal into its frequency-domain representation is the short-time fourier transform (STFT), which can be expressed by the following equation
10.1 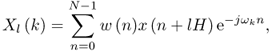
where ![]() is the complex spectrum of a given time frame,
is the complex spectrum of a given time frame, ![]() is the input sound,
is the input sound, ![]() is a complex sinusoid with frequency ωk expressed in radians,
is a complex sinusoid with frequency ωk expressed in radians, ![]() is the analysis window, l is the frame number, k is the frequency index, n is the time index, H is the time index hop size, and N is the FFT size.
is the analysis window, l is the frame number, k is the frequency index, n is the time index, H is the time index hop size, and N is the FFT size.
The STFT results in a general technique from which we can implement loss less analysis/synthesis systems. Many sound-transformation systems are based on direct implementations of the basic algorithm, and several examples have already been presented in previous chapters.
In this chapter, we extend the STFT framework by presenting higher-level modeling of the spectral data obtained with it. There are many spectral models based on the STFT that have been developed for sound and music signals ...
Get DAFX: Digital Audio Effects, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

